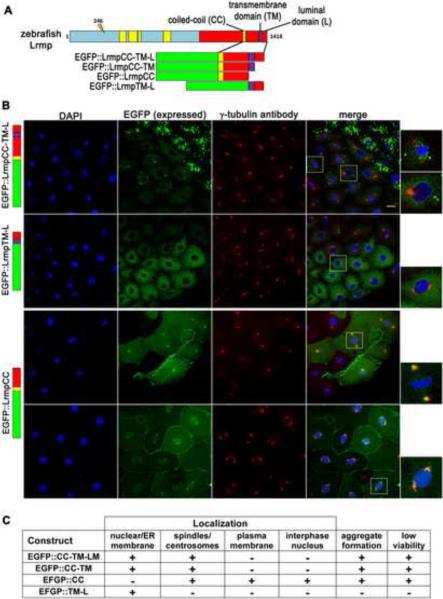
Figure 5. C-terminal domains of Lrmp facilitate subcellular targeting.
(A) Diagram of EFGP-fusion constructs. (B) Fusion construct RNAs encoding EGFP::LrmpCC-TM-L (top row), EGFP::LrmpTM-L (second row), and EGFP::LrmpCC construct (bottom two rows), were injected into one-cell wild-type embryos. Embryos expressing EGFP were fixed and processed for DAPI and anti-γ–tubulin immunostaining between 2.5-3.5 hpf. White boxes indicate fields shown at higher magnification (right). Scale bar represents 20 μm in all lower magnification panels. (C) Summary of results from EGFP::Lrmp C-terminal protein expression. Low viability (far right column) manifested as cell division defects and failure to undergo gastrulation, which lead to embryo lysis. See also Figure S5.