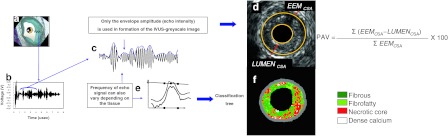
Fig. 1.
The ultrasound signal is generated in a piezoelectric crystal (asterisk) that transmits and receives sound waves (a). Ultrasound reflected by the tissue deforms crystal generating radiofrequency (RF) signal (b). Greyscale IVUS is derived from the amplitude of RF signal, discarding information beneath the peaks of the signal (c). Changes in the electric field of the piezoelectric crystal caused by ultrasound reflection is used to generate a grey-tone image (d). IVUS-RF analysis uses several additional spectral parameters to identify four plaque components (e). Plaque components that are identified are dense calcium (white), fibrous (green), fibro-fatty (greenish-yellow) and necrotic core (red) (f). PAV percentage atheroma volume, EEM external elastic membrane, CSA cross-sectional area