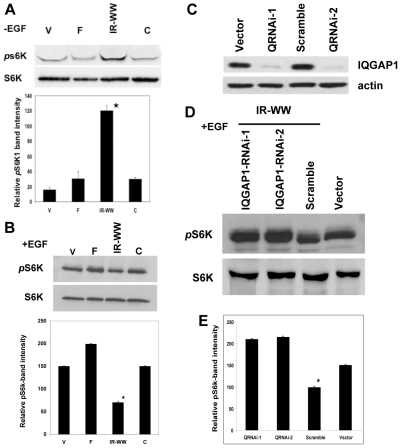
Fig. 4.
IQGAP1 modulates S6K1 T389 activity. (A) IQGAP1 stimulates S6K T389-P (pS6KT389) activity in high-serum (-EGF). Upper panel: a representative blot. Lysates from HeLa cells expressing the V5-IQGAP1 constructs and growing in full serum were blotted with total and phosphorylated Thr389 S6K1 antibodies. Lower panel: bands intensities were quantified by densitometry, normalized against total S6K and presented as the means ± s.e.m., n=3 independent experiments. *Significantly (P<0.001) lower than IQGAP1-F cells. (B) IQGAP1 attenuates S6K T389-P activity in response to EGF (+EGF): stable HeLa cell were serum-starved and treated with EGF and equal amount of lysates were processed and the band intensities quantified as in A. (C) Lysates from cells expressing two IQGAP1 siRNAs, which down regulate IQGAP1 by >90%. (D) Knockdown of endogenous IQGAP1 in cells expressing IQGAP1IR-WW and treated with EGF, restores the S6K T389-P level. Control and stable IQGAP1IR-WW HeLa cells expressing the IQGAP1 siRNAs were serum-starved and treated with EGF and their lysates blotted with antibodies for total and phosphorylated Thr389 S6K1. (E) Quantification by densitometry of the bands in D, presented as the means ± s.e.m., n=3 independent experiments. *Significantly (P<0.001) lower than the siRNA-treated cells. The results are representative of several cell lines including pancreatic β-cell and kidney cell lines.