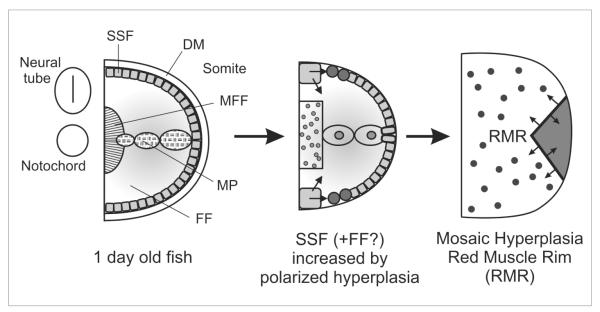
Figure 1.
Early myogenesis (left panel) generates four fibre types but leaves undifferentiated cells in the dermomyotome (DM), probably destined to support for later growth. Mononucleate superficial slow fibres (SSF) and muscle pioneer slow fibres (MP) form first, followed by multinucleate fast fibres (FF), a subset of which become specialised as medial fast fibres (MFF). Polarized hyperplasia (middle panel) generates further SSF and FF, probably from DM cells. Mosaic hyperplasia (right panel) arises from precursor cells scattered within the myotome and between the slow and fast regions at the so-called red muscle rim (RMR).