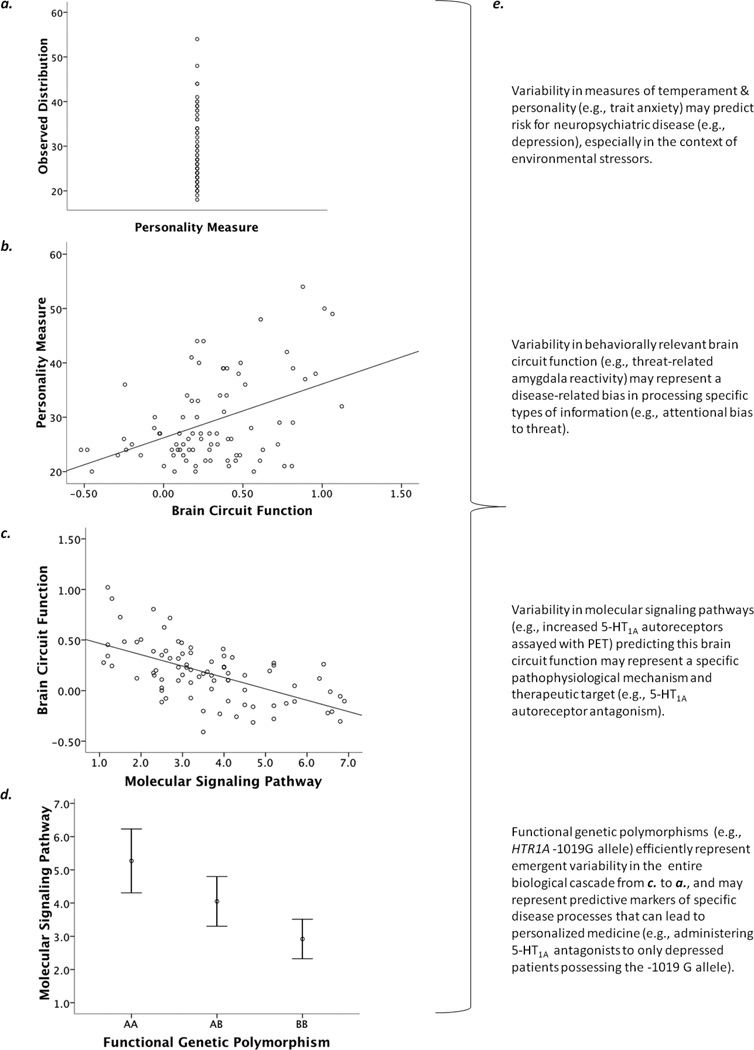
Figure 1.
Figure previously published in Annual Reviews of Neuroscience (Hariri, 2009). Integration of complementary technologies can be used to reveal the neurobiology of individual differences in complex behavioral traits. (a) Individual differences in personality and temperament are critical to shaping complex human behaviors and may serve as important predictors of vulnerability to neuropsychiatric disorders. (b) Neuroimaging technologies, especially BOLD fMRI, can identify links between variability in brain circuit function and individual differences in personality and temperament. (c) Multimodal PET/fMRI (or pharmacological fMRI) can map individual differences in behaviorally relevant brain circuit function to variability in specific molecular signaling pathways. (d) Variability in specific molecular signaling pathways can be mapped to functional genetic polymorphisms, which inform their ultimate biological origins and can be used to model efficiently how such emergent variability impacts behaviorally relevant brain function. (e) Each level of analysis can potentially inform clinically relevant issues, provide guiding principles for the development of more effective and personalized treatment options, and represent predictive risk markers that interact with unique environmental factors to precipitate disease.