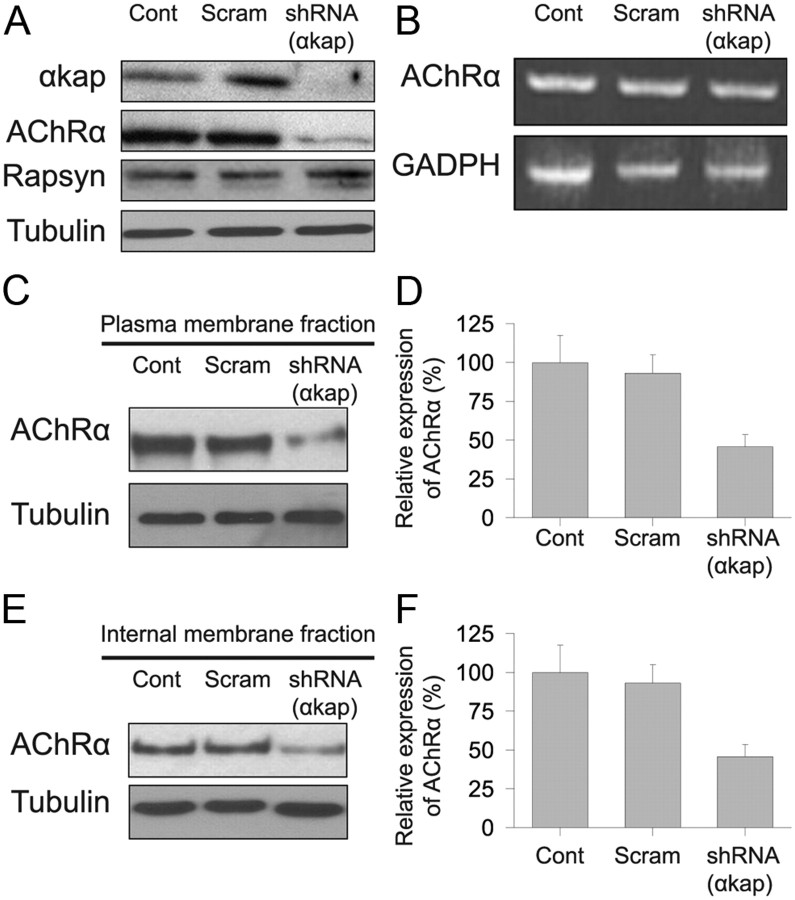
Figure 3.
Knockdown of αkap reduced AChR protein levels. A, Equal amounts of proteins from lysates of myotubes transfected with shRNA(αkap) or scrambled shRNA (Scram) or untransfected myotubes (Cont) were probed with four antibodies to assess the effect of the shRNA on αkap, AChRα, rapsyn, and tubulin. B, RT-PCR products of AChRα from cultured myotubes transfected with shRNA(αkap), scrambled shRNA, and untransfected myotubes. The PCR reaction conditions did not allow saturation to be reached for any of the samples, so band intensity is proportional to the amount of mRNA in the original sample. C, Western blots of surface AChRα. Living myotubes were treated with BTX–biotin at 4°C to saturate all surface receptors before cell lysis. Biotin-labeled surface AChRs were precipitated with NeutrAvidin beads. AChRα subunits were detected with MAB210. D, Quantification of three blots as in C. E, Western blots of intracellular AChRα. Surface receptors were saturated with unlabeled BTX, and then muscle lysates were saturated with BTX–biotin to selectively label intracellular AChR. F, Quantification of three blots as in E.