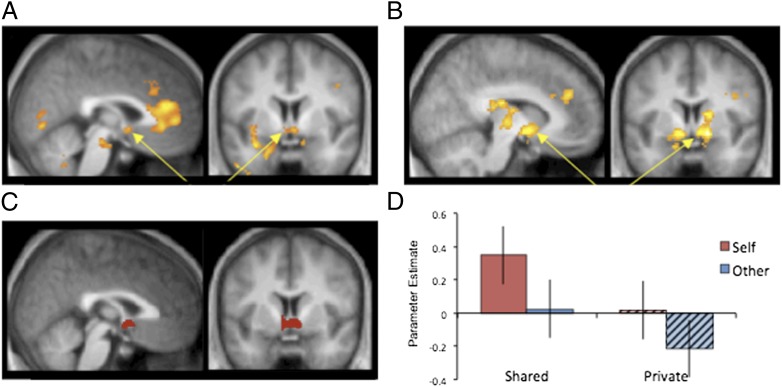
Fig. 3.
Introspecting about the self and disclosing that information to others serve as independent sources of reward. Whole-brain random-effects contrasts comparing (A) self > other and (B) shared > private from study 3 reveal significant reward activity in bilateral NAcc (P < 0.05, corrected; indicated by arrows). (C) A region of interest in bilateral NAcc, defined using the Monetary Incentive Delay task in the same set of subjects. (D) Parameter estimates from this independently defined region are graphically depicted for all four trial types: self shared (solid red), self private (dashed red), other shared (solid blue), and other private (dashed blue). Analyses of these parameter estimates confirmed that bilateral NAcc showed responses consistent with two independent sources of reward from self-disclosure: introspection about the self and sharing with others. Error bars depict SE calculated for within-subject designs.