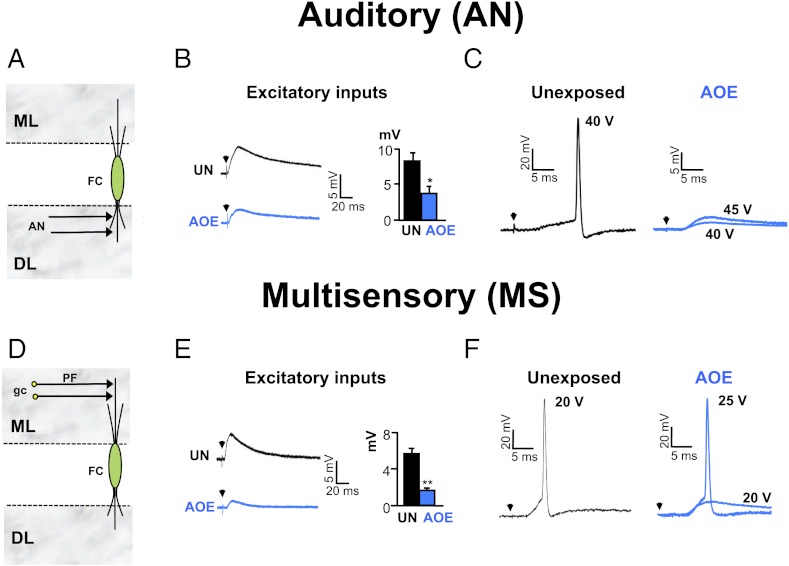
Fig. 1.
AOE down-regulates AN and MS synaptic transmission to FCs. (A) AN inputs directly terminate onto FC basal dendrites in the deep layer (DL). (B) AN stimulations (25 V, 0.3 Hz) trigger smaller EPSPs after AOE (blue). Membrane potential was −70 mV. Histogram summarizes EPSP amplitudes measured at similar stimulating voltages in unexposed (25 ± 4 V, n = 4) and exposed conditions (28 ± 2 V, n = 6). (C) In unexposed condition (black), AN stimulations (40 V, 0.3 Hz) trigger action potentials in a FC (membrane potential of −60 mV). After AOE (blue), AN stimulations (40–45 V, 0.3 Hz) fail to trigger action potentials. (D) MS inputs originate from parallel fibers (PF), which are the granule cell (gc) axons terminating onto FC apical dendrites in the molecular layer (ML). (E) MS stimulations (15 V, 0.3 Hz) trigger smaller EPSPs after AOE (blue). Membrane potential was −70 mV. Histogram summarizes EPSP amplitudes measured at similar stimulating voltages in unexposed (16 ± 1 V, n = 8) and exposed conditions (19 ± 2 V, n = 6). (F) In unexposed condition (black), MS stimulations (20 V, 0.3 Hz) trigger action potentials in a FC (membrane potential of −60 mV). After AOE (blue), higher stimulation voltages (25 V, 0.3 Hz) are required to trigger an action potential. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01: unpaired t tests.