Fig. 1.
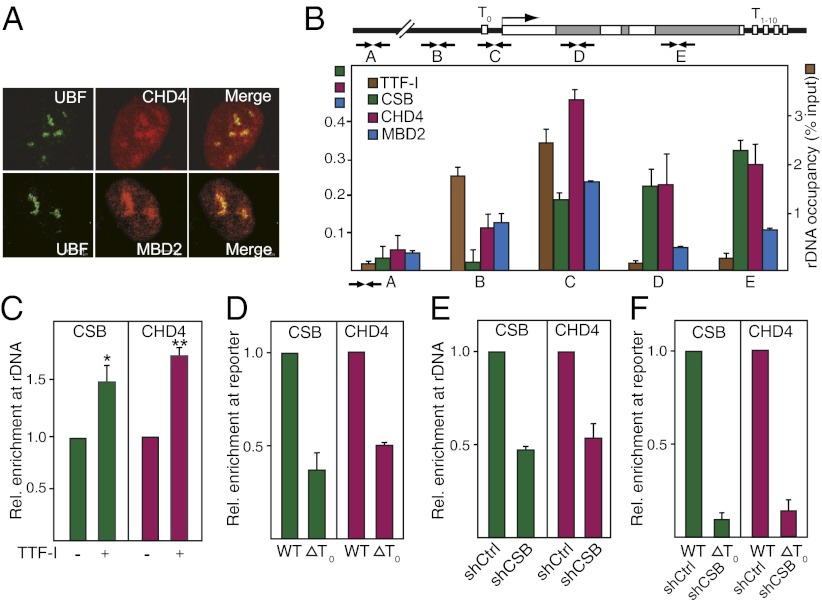
TTF-I recruits CHD4/NuRD to the rDNA promoter. (A) CHD4 and MBD3 localize in nucleoli. Immunofluorescent images of NIH 3T3 cells stained with antibodies against UBF, CHD4, and MBD2. (B) CHD4 is associated with rDNA. ChIP measuring rDNA occupancy of the indicated proteins in NIH 3T3 cells is shown. Bars show enrichment of CSB, CHD4, and MBD2 (Left y axis) and TTF-I (Right y axis) normalized to input DNA. Scheme indicates the position of primers used to amplify different regions of rDNA. White boxes mark the position of the terminators T0 and T1–10. Error bars denote SD (n = 3). (C) Overexpression of TTF-I increases CHD4 occupancy at rDNA. ChIP assay shows binding of CHD4 and CSB to the rDNA promoter after overexpression of EGFP-tagged TTF-I. *P value < 0.05, **P value < 0.01. (D) Binding of TTF-I to the promoter-proximal terminator T0 is required for targeting CHD4 to rDNA. NIH 3T3 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding Flag-tagged CHD4 and HA-tagged CSB together with the reporter plasmid pMr-1930-BH (WT) or pMr-1930ΔT0 (ΔT0). The association of CHD4 and CSB with the reporter plasmids was assayed by ChIP (n = 3). (E) Depletion of CSB impairs CHD4 binding to rDNA. ChIP shows the occupancy of CHD4 and CSB at the rDNA promoter in NIH 3T3 cells infected with retroviruses encoding shRNA against CSB compared with control shRNA (n = 3). (F) Recruitment of CHD4/NuRD to rDNA requires both TTF-I and CSB. NIH 3T3 cells infected with retroviruses encoding shRNA against CSB (shCSB) or control shRNA (shCtrl) were transfected with the reporter plasmid pMr-1930-BH (WT) or pMr1930ΔT0 (T0). The association of CHD4 and CSB with the reporter plasmids was assayed by ChIP (n = 3).