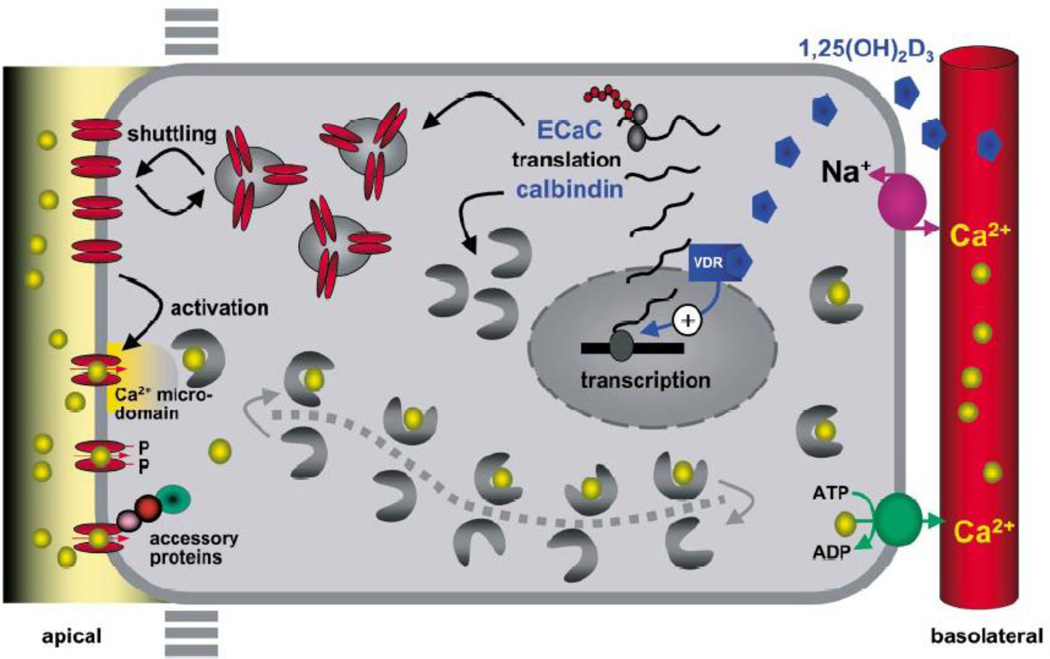
Figure 2.
Integrated model of active Ca2+ reabsorption in the distal part of the nephron. Apical entry of Ca2+ is facilitated by ECaC. Ca2+ then binds to calbindin-D28K, and this complex diffuses through the cytosol to the basolateral membrane, where Ca2+ is extruded by a Na+/Ca2+ exchanger and a plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase. The individually controlled steps in the activation process of the rate limiting Ca2+ entry channel include 1α,25(OH)2D3-mediated transcriptional and translational activation, shuttling to the apical membrane, and subsequent activation of apically located channels by ambient Ca2+ concentration, direct phosphorylation and/or accessory proteins. (With permission from Hoenderop, et al [268])