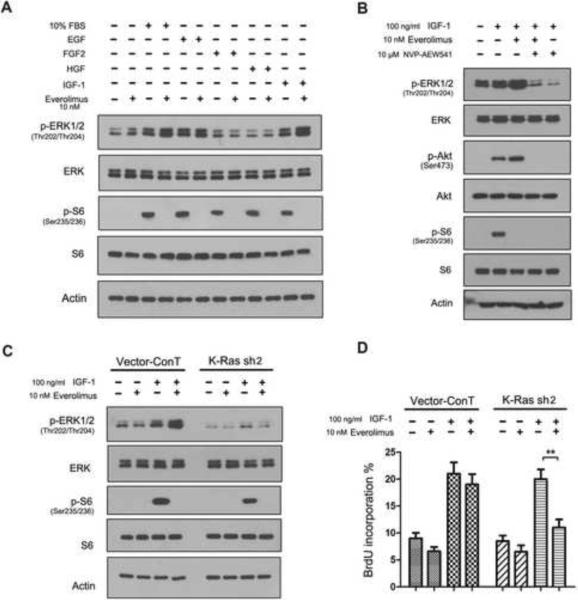
Figure 7.
K-Ras mutations contribute to the everolimus-induced ERK signal. (A) The K-Ras mt PANC-1 cells were subjected to western blotting after treated first with everolimus and then exposed to 10% FBS, EGF, FGF2, HGF and IGF-1, as indicated on the top of the panel. (B) The experiment was repeated with using NVP-AEW541. (C) The empty vector and K-Ras shRNA expressing PANC-1 cells were examined by western blotting after treated first with everolimus first and then with IGF-1. (D) The empty vector and K-Ras shRNA expressing PANC-1 cells, treated as described above in B, were examined by by BrdU labeling assay. The experiment was repeated three times and the data was presented as mean ± SD. **, p < 0.01.