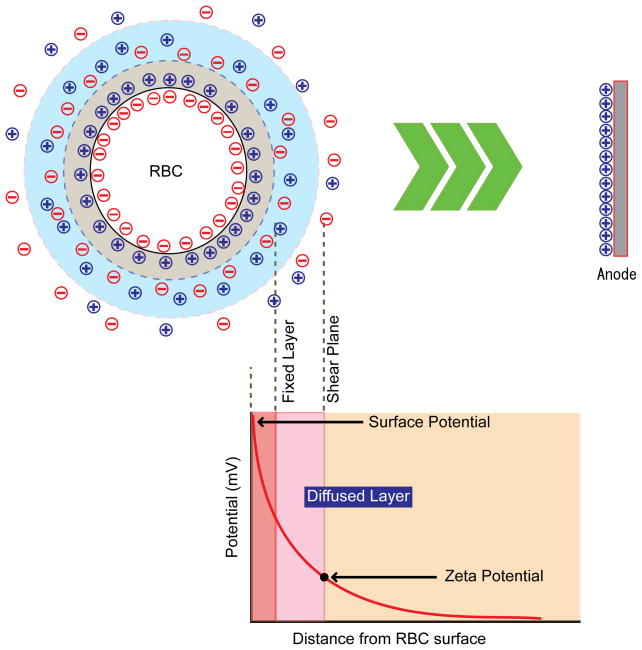
Figure 1.
Basic concept of zeta potential (ZP). Negatively-charged red blood cells migrate toward the positive electrode upon the application of voltage between positive and negative electrodes. ZP is defined as and , where A is a constant, ζ is the zeta potential, η is the viscosity of solution, ε is the dielectric constant, and U is the electrophoretic mobility, ν is the speed of particle, V is the applied voltage, and L is the distance of electrode (Overbeek, 1952, Weiss and Woodbridge, 1967). Dielectric constant and viscosity of the buffer is approximated as those of water.