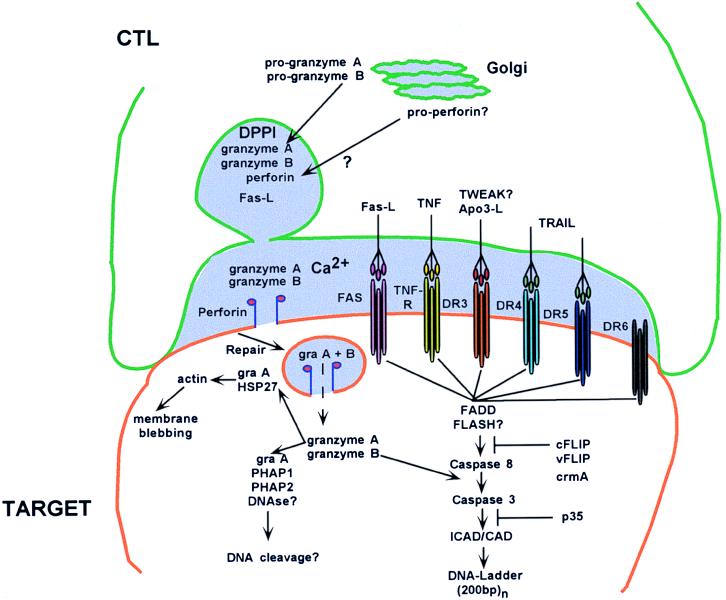
Figure 1.
CTL cytotoxic mechanisms. The killer cell has formed a conjugate “synapse” with the target cell and is in the process of secreting granules (light purple) in the synaptic space. Granule material including perforin is derived from the Golgi complex; granzymes are processed by DPPI and stored in the granule. After secretion into the synaptic space and pore formation, granzymes enter into the target cell through repair endocytosis. Granzyme B activates downstream apoptotic pathways, whereas granzyme A may activate caspase-independent apoptosis. TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TWEAK?, ligand in the TNF family that weakly induces apoptosis; TRAIL, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; DRn, death receptor n; gra, granzyme; PHAPn, putative HLA-associated protein n; FADD, FAS-associated death domain factor; FLASH?, FLICE-associated huge protein; ICAD/CAD, inhibitor caspase-activated DNase/caspase-activated DNase; cFLIP, cellular FLICE inhibitory protein; vFLIP, viral FLICE inhibitory protein; crmA, cytokine response modifier A.