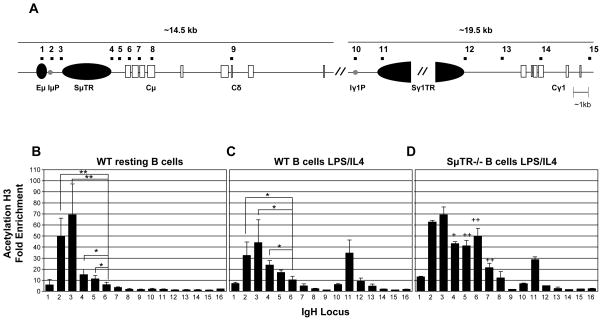
Figure 2. Acetyl H3 localizes to specific segments of the Ig heavy chain μ and γ1 regions in splenic B cells.
(A) Diagram of the Ig heavy chain locus. Black squares above the diagram mark locations of PCR primer pairs in the ChIP analyses; primer pair 16 is for a control gene, β-globin (Chowdhury and Sen, 2003; Garrett et al., 2005). Black vertical oval depicts the Eμ enhancer. Black horizontal ovals depict switch sequence, whereas white rectangles depict constant segments. Gray circles depict promoter regions. Two slashes depict sequence gaps. (B). Acetyl H3 at the IgH μ and γ1 loci in WT resting splenic B cells, n=4. (C). Acetyl H3 at the IgH μ and γ1 loci in WT splenic B cells stimulated with LPS and IL4 for 48 hours, n=4. (D). Acetyl H3 at the IgH μ and γ1 loci in SμTR−/− splenic B cells stimulated with LPS and IL4 for 48 hours, n=2. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation was performed with antibody specific for acetylated histone 3. Real-time PCR was performed in triplicate on input and antibody bound ChIP fractions. Fold enrichment of each DNA sequence in an IP sample relative to an Input sample is shown. Values were averaged; standard deviations are shown as error bars. Student t-test statistical analysis was performed. * or + indicates p-value < 0.05, ** or ++ indicates p-value < 0.01. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences between different DNA segments. Crosses (+) indicate significant differences between SμTR−/− B cells LPS/IL4 and WT B cells LPS/IL4 48 within the same DNA segments.