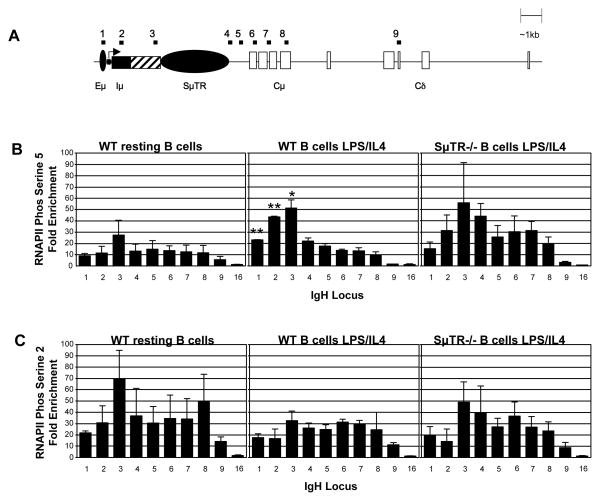
Figure 5. Enrichment of RNAPII at the Immunoglobulin heavy chain μ locus in splenic B cells.
(A) Diagram of the Ig heavy chain μ locus as in Fig. 2. The solid box represents the Iμ exon. The hatched box represents the region containing the Iμ splice site as well as other promoters and splice sites that are sufficient to provide significant CSR in mutant mice that lack either the Iμ promoter (Bottaro et al., 1998) or the Iμ splice site (Kuzin et al., 2000). (B) Association of RNAPII Phos serine 5 (transcriptional initiation) at the IgH μ locus in WT resting splenic B cells (n=3), WT splenic B cells stimulated with LPS and IL4 for 48 hours (n=2), and SμTR−/− splenic B cells stimulated in with LPS and IL4 for 48 hours, (n=2). (C) Association of RNAPII Phos serine 2 (transcriptional elongation) at the IgH μ locus in WT resting splenic B cells (n=2), WT splenic B cells stimulated in culture with LPS and IL4 for 48 hours (n=3), and SμTR−/− splenic B cells stimulated in culture with LPS and IL4 for 48 hours, (n=3). Chromatin Immunoprecipitation was performed on freshly isolated B cells or after LPS/IL4 stimulation for 48 hours with antibody specific for RNAPII phosphorylated on serine 5 or serine 3. Analyses and data presentation are similar to Fig. 2. * Indicates p-value < 0.05, ** indicates p-value < 0.01. Asterisks (*) indicate significant differences between WT B cells LPS/IL4 and WT resting B cells within the same DNA segment.