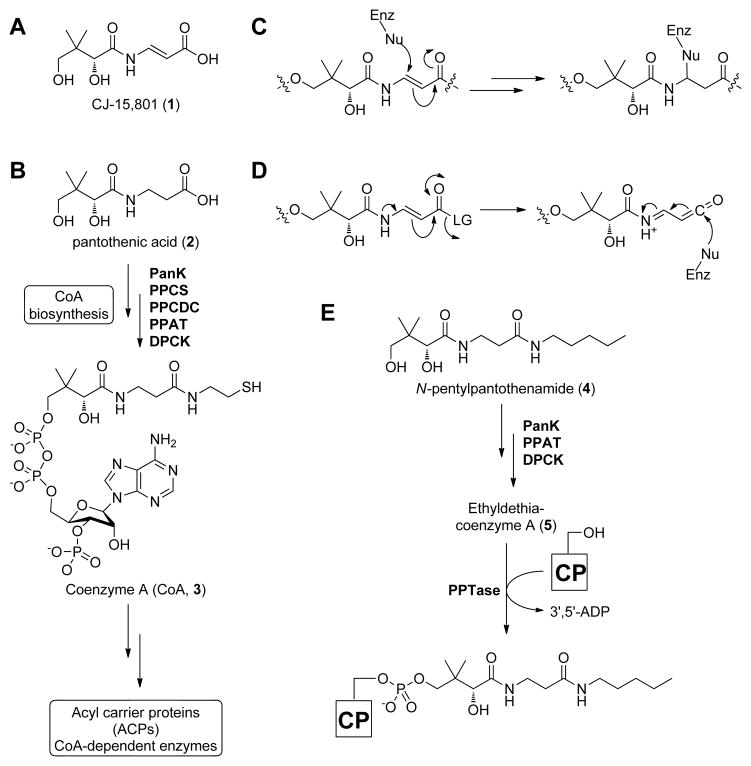
Figure 1. Structures of the antibiotic CJ-15,801 (1), selected coenzyme A biosynthetic intermediates, antimetabolites, and intermediate mimics.
(A) Structure of the CJ-15,801 (1).
(B) Biosynthesis of CoA (3) from pantothenic acid (2). PanK, pantothenate kinase; PPCS, phosphopantothenoylcysteine synthetase; PPCDC, phosphopantothenoylcysteine decarboxylase; PPAT, phosphopantetheine adenylyltransferase; DCPK, dephospho-coenzyme A kinase.
(C) Proposed mechanism for irreversible inhibition by CJ-15,801 acting as an electrophilic trap.
(D) Proposed mechanism for irreversible inhibition by CJ-15,801 after its transformation into a ketene intermediate.
(E) Biotransformation of the pantothenic acid analogue N-pentylpantothenamide (4) to the CoA antimetabolite ethyldethia-CoA (5), which has the catalytically essential thiol of the cofactor replaced by a propyl group. The antimetabolite subsequently serves as donor in the phosphopantetheinyl transferase (PPTase)-catalyzed post-translational modification of acyl and peptidyl carrier proteins (CPs), which results in similarly inactive crypto-CPs.