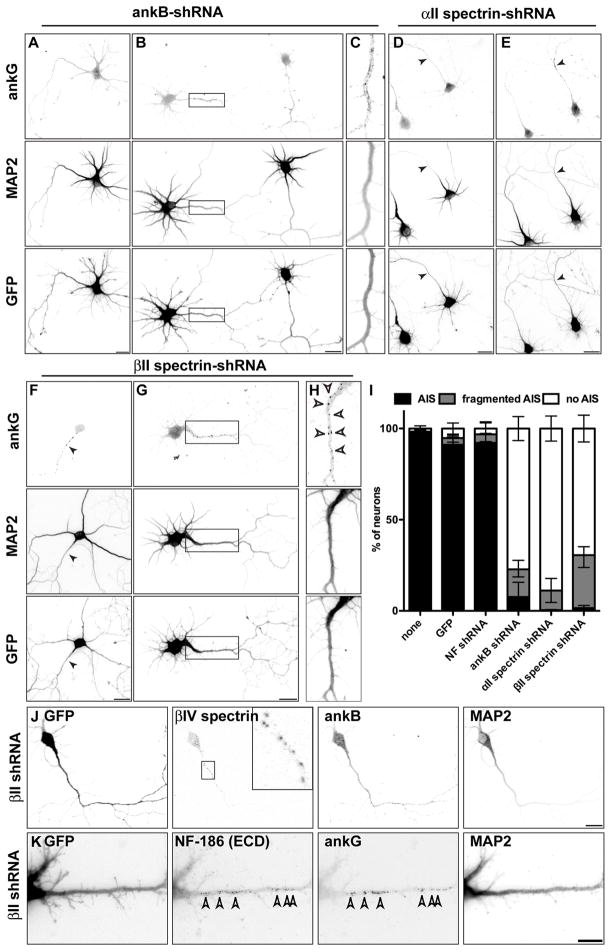
Figure 5. Loss of ankB, αII spectrin, or βII spectrin inhibits ankG clustering.
(A–H) Hippocampal neurons infected at DIV 0 with ankB-shRNA (A–C), αII spectrin-shRNA (D–E), and βII spectrin-shRNA (F–H) adenovirus and immunostained for ankG, MAP2, and GFP at DIV7. Boxes in (B) and (G) corresponds to panels (C) and (H), respectively. Scale bars, 20 μm.
(I) Quantification of the staining patterns for ankG. Data are mean ± SD. The total number of neurons counted was 467 (none), 402 (GFP), 426 (NF shRNA), 571 (ankB shRNA), 502 (αII spectrin shRNA), and 526 (βII spectrin shRNA).
(J–K) Neurons infected at DIV 0 with βII spectrin-shRNA adenovirus and immunostained for GFP, βIV spectrin, ankB, and MAP2 (J) or GFP, NF-186 ectodomain (ECD), ankG, and MAP2 (K) at DIV 7. Scale bars, 20 μm.