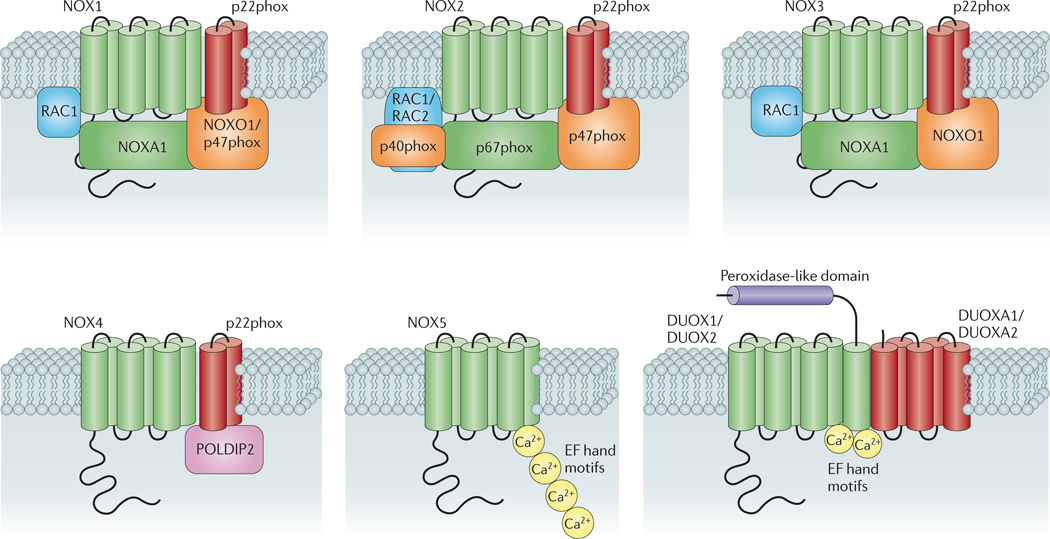
Figure 1. Subunit composition of the seven mammalian NADPH oxidase isoforms.
The catalytic core subunits of the enzymes (NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1)–NOX5, dual oxidase 1 (DUOX1) and DUOX2) are shown in green; NOX and DUOX maturation and stabilization partners (p22phox, DUOX activator 1 (DUOXA1) and DUOXA2) are shown in red; cytosolic organizers (p40phox, NOX organizer 1 (NOXO1) and p47phox) are shown in orange; cytosolic activators (p67phox and NOX activator 1 (NOXA1)) are shown in green; and small GTPases (RAC1 and RAC2) are shown in blue. Also shown (in pink) is polymerase δ-interacting protein 2 (POLDIP2), which is thought to regulate NOX4 activity and link production of reactive oxygen species by this isoform with cytoskeletal organization80. EF hand motifs (yellow circles) are also shown, which bind to Ca2+ and thereby regulate the activity of NOX5, DUOX1 and DUOX2 oxidases. The figure also illustrates the putative additional amino-terminal transmembrane domain and extracellular peroxidase-like region (shown in purple) on DUOX1 and DUOX2. Although NOX3 oxidase activity is enhanced by the expression of organizer and activator proteins, the enzyme displays constitutive activity in their absence.