Abstract
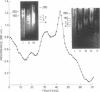
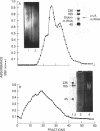
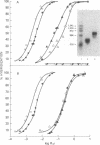
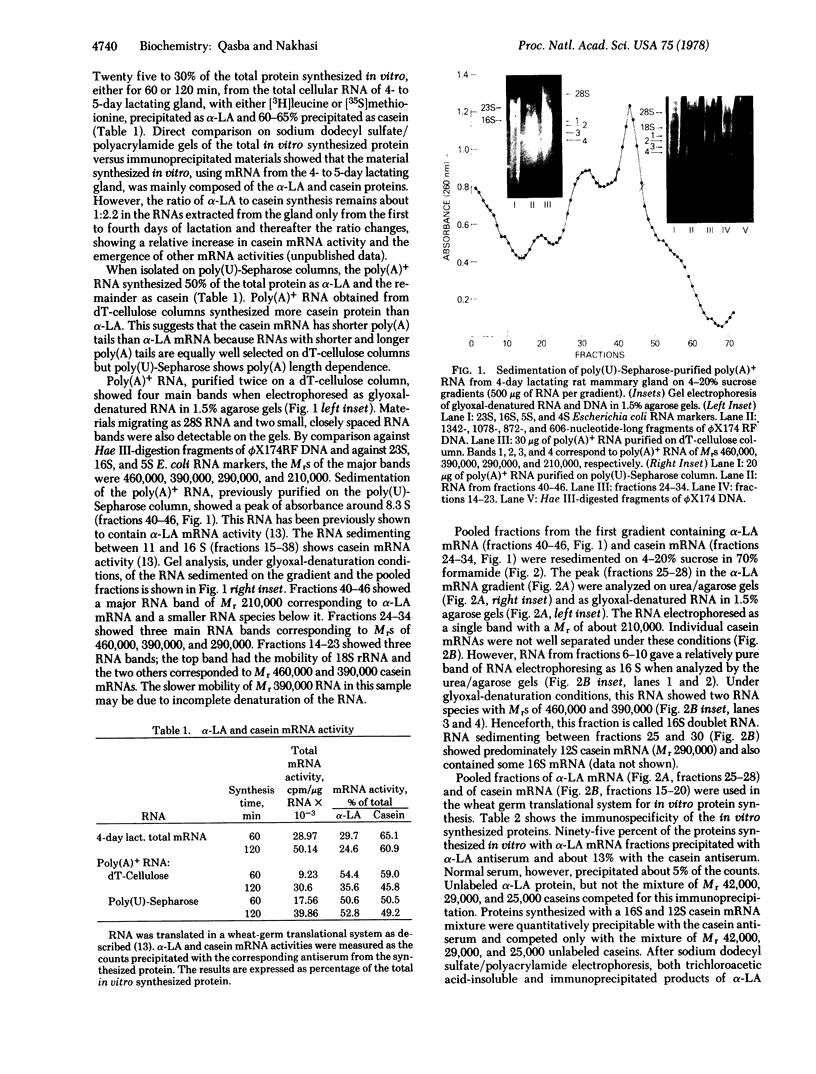
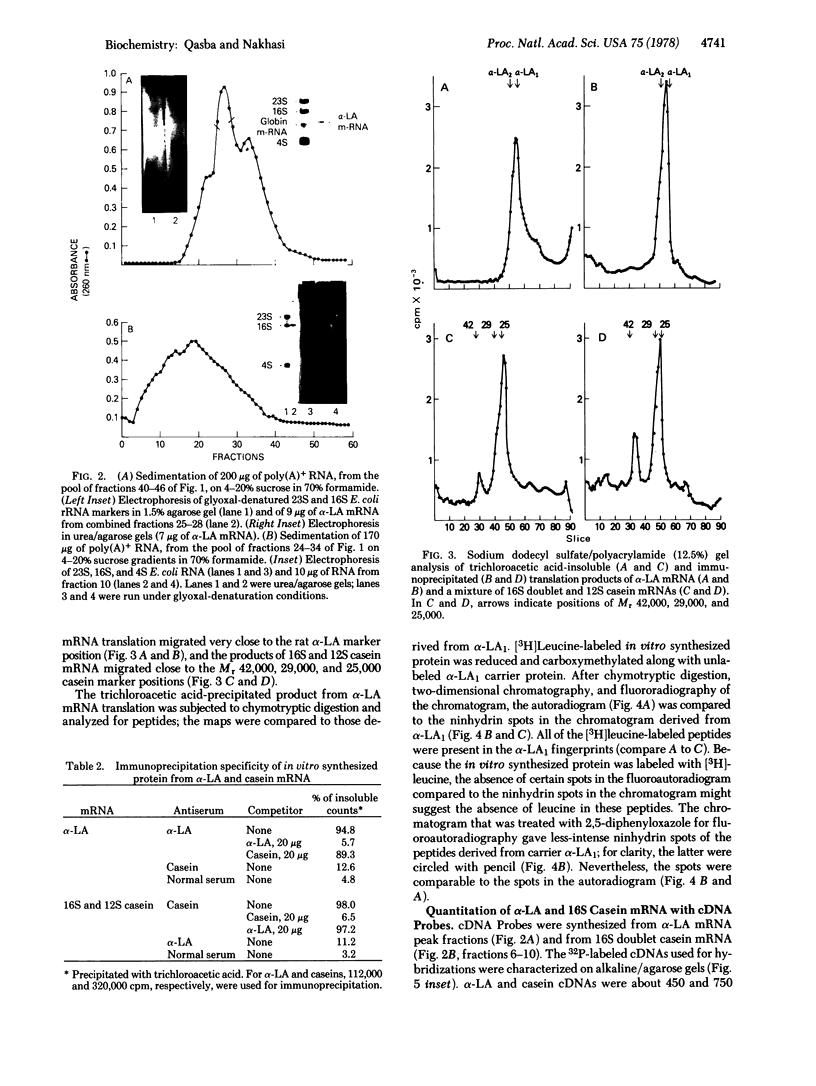
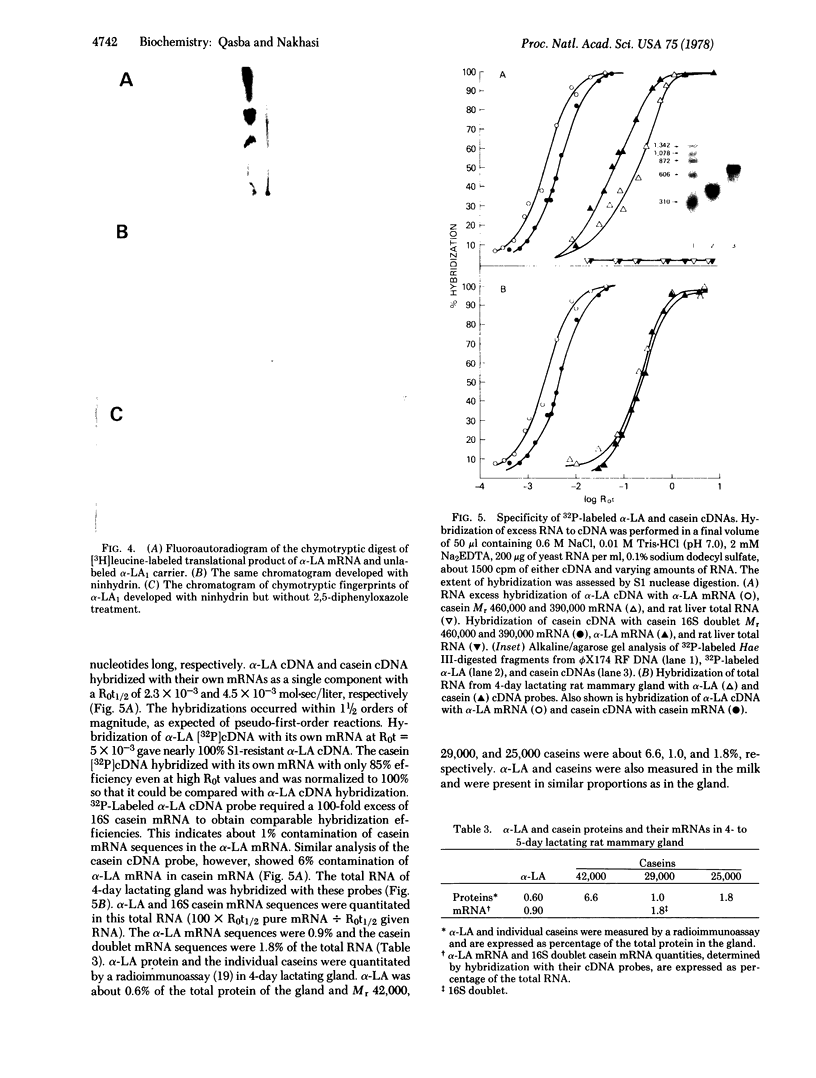
Rat alpha-Lactalbumin (alpha-LA) mRNA has been purified from the total RNA of 4-day lactating mammary gland by poly(U)-Sepharose chromatography and by fractionation of the poly(A)+ RNA on sucrose gradients. alpha-LA mRNA was homogeneous as judged by electrophoresis in urea/agarose gel and in 1.5% agarose gel under glyoxal-denaturation conditions, which gave a molecular weight of 210,000. The chymotryptic fingerprints of the protein synthesized with this mRNA, in a translational system derived from wheat germ, were similar to those of purified rat alpha-LA. In rat milk or lactating gland, the content of Mr 42,000 casein is 6 times greater than that of Mr 29,000 casein and 10 times greater than that of alpha-LA. However, alpha-LA mRNA (Mr 210,000) and two casein mRNas (Mr 460,000 and 390,000), coding for Mr 42,000 and 29,000 caseins, were present in equal proportions when measured with cDNA probes in the total RNA of 4- to 5-day lactating gland. Moreover, alpha-LA and total casein were synthesized in a ratio fo 1:2.5 in a wheat-germ translational system using the total RNA of the lactating gland. The results suggest post-transcription controls in the synthesis of these proteins.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baglioni C. Nonpolysomal messenger RNA. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Nov 29;241(0):183–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb21877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brew K., Hill R. L. Lactose biosynthesis. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1975;72:105–158. doi: 10.1007/BFb0031548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. C., Fish W. W., Hudson B. G., Ebner K. E. Isolation and characterization of rat alpha-lactalbumin: a glycoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 28;491(1):82–92. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90043-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabartty P. K., Qasba P. K. Partial purification of rat alpha-lactalbumin mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jun;4(6):2065–2074. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.6.2065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R. K., Brown P. A., Harrison O. S., McIlreavy D., Campbell P. N. Guinea-pig milk-protein synthesis. Isolation and characterization of messenger ribonucleic acids from lactating mammary gland and identification of caseins and pre-alpha-lactalbumin as translation products in heterologous cell-free systems. Biochem J. 1976 Oct 15;160(1):57–74. doi: 10.1042/bj1600057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeley R. G., Gordon J. I., Burns A. T., Mullinix K. P., Binastein M., Goldberg R. F. Primary activation of the vitellogenin gene in the rooster. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 25;252(22):8310–8319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRIFFITH D. R., TURNER C. W. Normal growth of rat mammary glands during pregnancy and early lactation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Feb;106:448–450. doi: 10.3181/00379727-106-26365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S. Gel electrophoretic separation of the complementary strands of bacteriophage DNA. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):342–344. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80042-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houdebine L. M., Gaye P. Purification of the mRNAs for Ewe alphaS-casein and beta-casein by immunoprecipitation of polysomes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 16;63(1):9–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalan E. B., Greenberg R., Thompson M. P. Analysis of proteolytic digests of genetic variants of alpha-s1-Casein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 9;115(3):468–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90065-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNFORD R. E. CHANGES IN THE MAMMARY GLANDS OF RATS AND MICE DURING PREGNANCY, LACTATION AND INVOLUTION. 1. HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURE. J Endocrinol. 1963 Dec;28:1–15. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0280001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Topper Y. J. Hormone-dependent accumulation of rough endoplasmic reticulum in mouse mammary epithelial cells in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 25;246(24):7701–7707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qasba P. K., Chakrabartty P. K. Purification and properties of two forms of rat alpha-lactalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1167–1173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qasba P. K., Gullino P. M. alpha-Lactalbumin content of rat mammary carcinomas and the effect of pituitary stimulation. Cancer Res. 1977 Oct;37(10):3792–3795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. M. Isolation and characterization of purified rat casein messenger ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 30;15(24):5263–5271. doi: 10.1021/bi00669a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. M., Woo S. L., Comstock J. P. Regulation of casein messenger RNA during the development of the rat mammary gland. Biochemistry. 1975 Jul;14(13):2895–2903. doi: 10.1021/bi00684a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topper Y. J. Multiple hormone interactions in the development of mammary gland in vitro. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1970;26:287–308. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571126-5.50011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]