Figure 4.
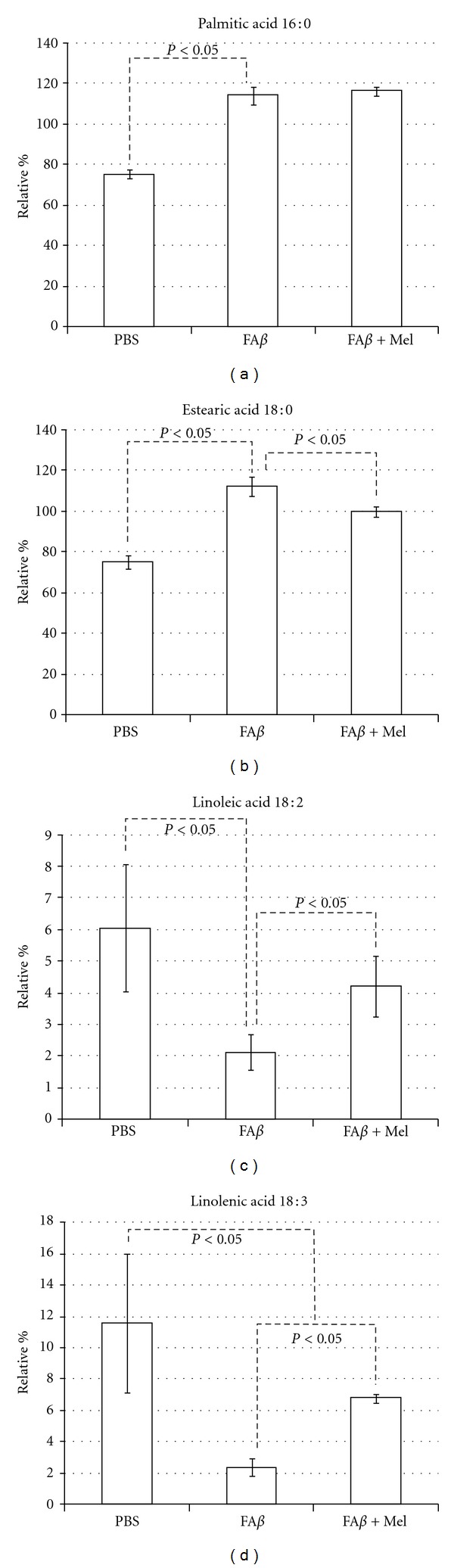
Aβ and H2O2 (not shown) had similar and highly significant effects on saturated fatty acids particularly on palmitic and estearic acids whose percentages were increased 39 and 37% correspondingly. Linoleic acid was reduced to a third from the control, while linolenic acid was reduced to less than a quart from the control value, as shown. These important effects of Aβ on specific saturated and unsaturated fatty acids affected the unsaturated/saturated (U/S) balance.
