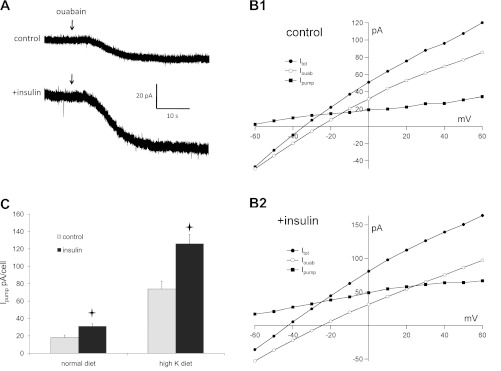
Fig. 1.
Insulin upregulates Na/K pump activity in principal cells of the rat cortical collecting duct (CCD). A: responses to ouabain administration with the cell voltage clamped to 0 mV in a control cell and a cell treated with insulin from an animal on normal chow. Initial outward currents before ouabain addition were 21 and 65 pA, respectively. B: pump-mediated current-voltage (I-V) relationships from principal cells of an animal on normal chow. Data were obtained from a control cell (B1) and a cell treated with insulin (B2). Currents were measured at steady state in the absence (Itot; ●) and presence (Iouab; ○) of 1 mM ouabain. The difference current (Ipump; ■) represents charge moved through the pump. C. summary of Ipump measured at 0 mV in control and insulin-treated cells from animals on control or high-K diets. Values are means ± SE for 13 cells (control diet) and 9–11 cells (high-K diet). *Statistical significance (P < 0.05 vs. control values).