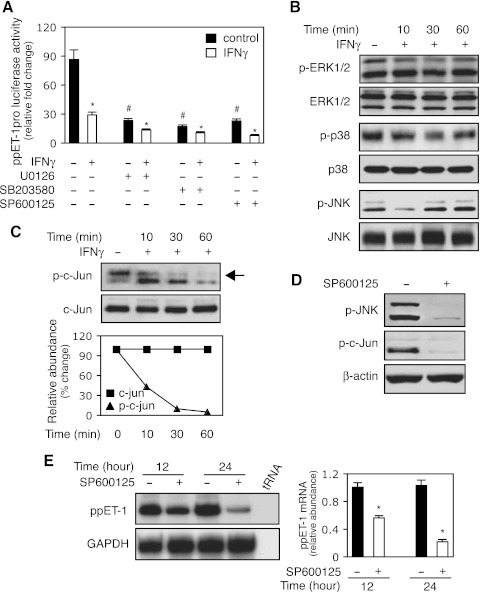
Fig. 3.
The JNK/c-Jun pathway mediates IFNγ-induced inhibition of ppET-1 transcription. A: HSCs were transduced with a ppET-1 promoter/luciferase reporter construct (ppET-1–2121+131) and preexposed to U0126 (10 μM, MEK/ERK inhibitor), SB203580 (10 μM, p38-MAPK inhibitor) or SP600125 (10μM, JNK inhibitor) for 30 min followed by the addition of IFNγ (500 IU/ml). Luciferase activity was measured (n = 3; *P < 0.05 vs. corresponding control with no IFNγ; #P < 0.05 vs. no IFNγ). B: HSCs were incubated in 0.2% serum medium with or without IFNγ (1,000 IU/ml) for the indicated times, and whole cell extracts were subjected to immunoblotting with antibodies to detect phospho-ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2), ERK1/2, phospho-p38 (p-p38), p38, phospho-JNK (p-JNK) and JNK. Representative images of 3 others are shown. C: stellate cells were incubated in 0.2% serum medium with or without IFNγ (1,000 IU/ml) as in (B), and whole cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot with anti-phospho-c-Jun (p-c-Jun) or c-Jun antibodies. Quantitative data are shown (bottom, n = 3). D: stellate cells were exposed to SP600125 (SP, 10 μM) for 30 min, and cell lysates were immunoblotted with p-JNK (top) or p-c-Jun (middle). E: HSCs were incubated in 0.2% serum medium with or without SP600125 (10μM) for the indicated times. PreproET-1 mRNA was detected as in materials and methods, and signals corresponding to specific bands were normalized to control GAPDH mRNA signals. The quantitative data are presented graphically (deviation = 3; *P < 0.05 vs. control).