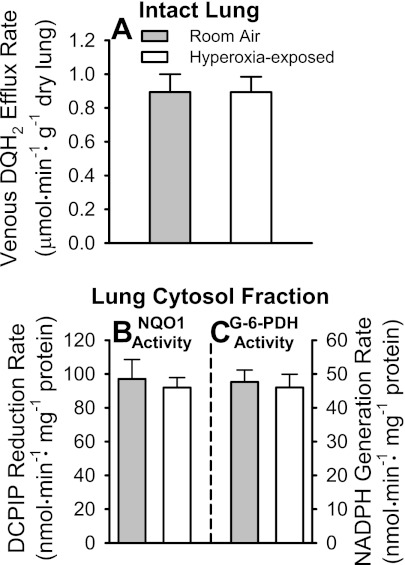
Fig. 6.
Pulmonary venous duroquinone (DQ) hydroquinone (DQH2) efflux rates during DQ infusion into pulmonary arterial inflow of room air- and hyperoxia-exposed NQO1+/+ mouse lungs, and lung cytosol fraction NQO1 and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PDH) activities. A: steady-state pulmonary venous DQH2 efflux rates during 50 μM DQ infusion into pulmonary arterial inflow. B: lung cytosol fraction NQO1 activities for lungs in A. DCIP, 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol. C: lung cytosol fraction G-6-PDH activities for lungs in A. Values are means ± SE; n = 5 room air- and 6 hyperoxia-exposed lungs. There were no statistically significant differences (by t-test) between values within A, B, or C.