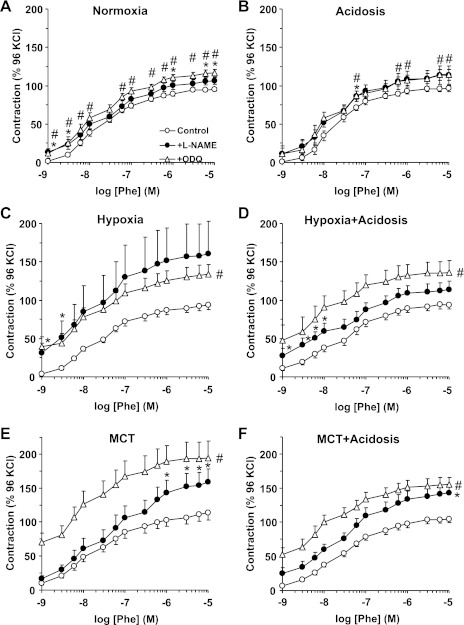
Fig. 7.
Phe-induced contraction as % of Ca2+-dependent 96 mM KCl-induced contraction during blockade of the NO-cGMP pathway in pulmonary artery of normoxic, hypoxic, and MCT-treated rats with or without treatment with NH4Cl (acidosis). Pulmonary artery segments of control normoxic (A), normoxic+acidosis (B), hypoxic (C), hypoxic+acidosis (D), MCT-treated (E), and MCT+acidosis rats (F) were either nontreated (○) or pretreated with the NOS inhibitor l-NAME (3 × 10−4 M; ●) or the guanylate cyclase inhibitor ODQ (10−5 M; ▵) for 10 min. The tissues were stimulated with increasing concentrations of Phe, and the contractile response was measured and presented as % of the control Ca2+-dependent 96 mM KCl-induced contraction. Data represent means ± SE (n = 6–8). *Measurements in l-NAME-treated pulmonary artery segments are significantly different (P < 0.05) from corresponding measurements in nontreated segments. #Measurements in ODQ-treated pulmonary artery segments are significantly different (P < 0.05) from corresponding measurements in nontreated segments.