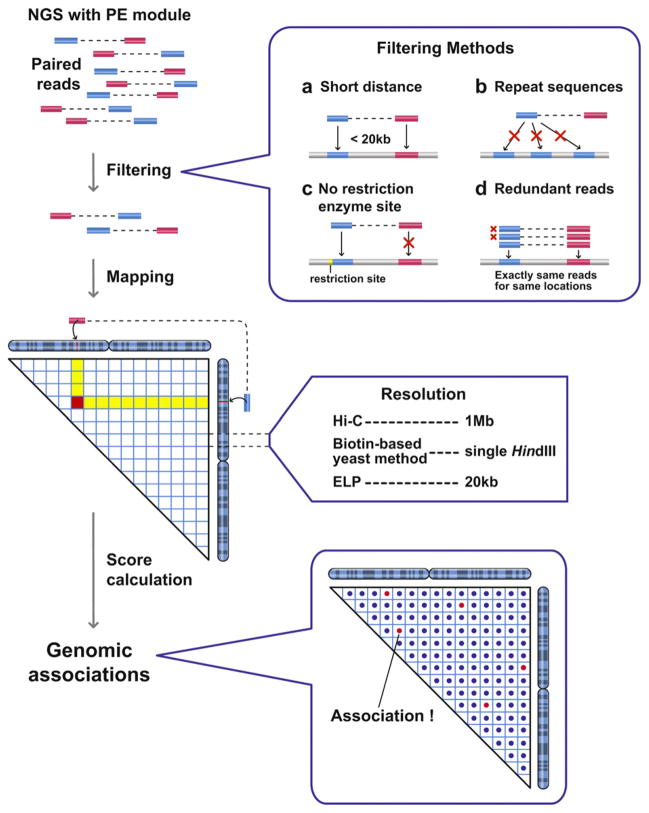
Fig. 2.
Processing of 3C-seq raw data to detect genome-wide associations. NGS with PE module provides more than 10 million paired sequence information for hybrid DNA molecules, which reflect genomic associations. Those paired-end reads are mapped to genomic positions, and reads are eliminated based on four different filtering processes (labeled a–d). The paired-end reads reflect short-range associations (a), and associations involving repetitive DNA sequences (b) are eliminated. The paired reads assigned to regions where restriction enzyme sites are not present nearby are also eliminated, because it is not clear how these hybrid DNA molecules are produced during the 3C-seq procedures (c). The redundant paired-end reads with the exact same sequences are counted as a single hybrid molecule to avoid PCR bias (d). The remaining paired-end reads are then examined to identify long-range genomic associations. Numbers of paired-end reads assigned to genomic combinations are used for score calculation.