Fig. 4. Airway epithelial H+ and HCO3- transport determines ASL pH.
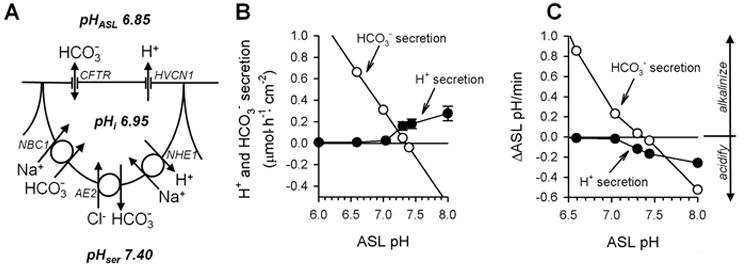
A. Distribution of H+ and HCO3- transporters in lung epithelium. The HVCN1 H+ conductance and the CFTR HCO3- conductance are expressed apically. HVCN1 conducts H+ only outwardly while CFTR conducts HCO3- both ways. The Na+-H+ exchanger NHE1, the Cl--HCO3- anion exchanger AE2, and the Na+-HCO3- cotransporter NBC1 are present in the basolateral membrane. Resting pH values for the airway surface liquid (pHASL), intracellularly (pHi), and serosally (pHser) are given. For stoichiometry of transporters see (28, 78). B. ASL pH determines airway H+ and HCO3- secretion. HCO3- secretion (open symbols) is modeled for pHi 6.95; Va -24 mV; apical, linear, voltage-independent HCO3- conductance 0.4 mS/cm2; average pCO2 3 kPa. H+ secretion data (filled symbols) are mean±SE compiled from previous measurements (17, 19). C. Predicted change of ASL pH by H+ and HCO3- secretion. Calculated from rates in B using buffer capacities for the ASL from ref. (65) (range 6.5 to 15 mM/pH) and an ASL volume of 1.5 μl/cm2. CFTR, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator.
