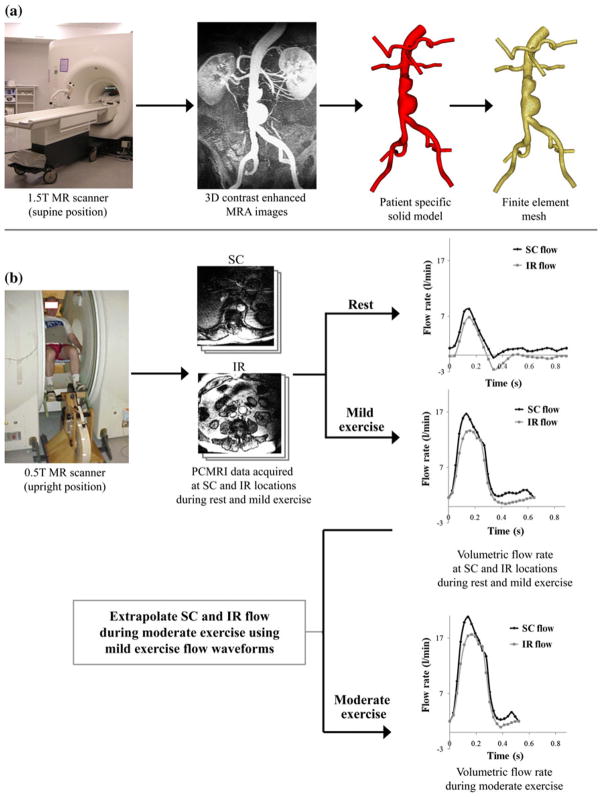
FIGURE 1.
Data acquisition using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). (a) AAA subjects were scanned in the supine position using a 1.5 T Signa MR scanner (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee WI). We used a 3D gadolinium-enhanced MRA sequence to image the lumen of the abdominal aorta. Custom software37 was used to process these images, construct a 3D solid model, and generate a finite element mesh based on the model geometry (MeshSim™, Simmetrix, Clifton Park, NY). (b) In a separate imaging study, AAA subjects were scanned in the upright position using a 0.5 T Signa MR scanner (GE Medical Systems, Milwaukee, WI). We acquired cine phase-contrast MRI (PC-MRI) data at supraceliac (SC) and infrarenal (IR) locations during rest and performing lower-extremity mild exercise using an MR-compatible exercise cycle. The PC-MRI images were used to calculate the time-dependent volumetric flow rate at SC and IR locations with 24 time points per cardiac cycle. SC and IR flow waveforms at the moderate exercise level were extrapolated from the SC and IR flow waveforms obtained during mild exercise.