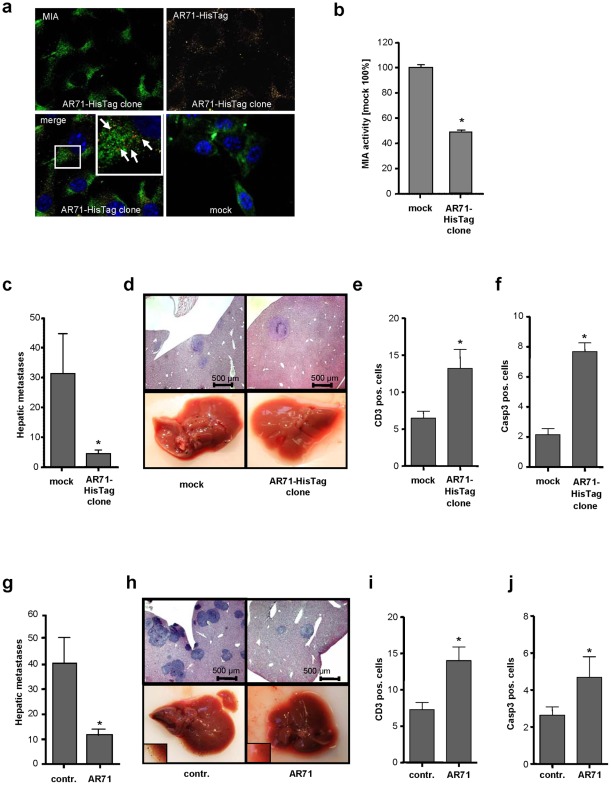
Figure 3. Effect of MIA inhibitory peptide AR71 on the formation of metastases in vivo.
(a) Immunofluorescence studies of murine B16 melanoma cells stably transfected with an AR71-HisTag construct, with MIA (FITC) shown in green and AR71-HisTag (TRITC) shown in yellow. Co-localization is depicted in red and is indicated by white arrows. The excess of MIA not co-localized with AR71 is due to the internalization of exogenous MIA by the melanoma cells [29]. The mock control did not include AR71-HisTag. (b) Murine B16 AR71-HisTag clones were analyzed for their migratory activity in a Boyden chamber assay. Compared to the mock control, the AR71-HisTag-expressing cell clone displayed drastically reduced migration by reducing MIA activity. (c) The AR71-HisTag clone and a corresponding mock control were injected into the spleens of Bl/6N mice (n = 8 each). Histological analysis revealed that AR71-HisTag clones formed significantly fewer hepatic metastases than the mock control cells did. (d) Representative histological liver sections (upper row) and macroscopic pictures (lower row) of mice injected with the mock control and an AR71-HisTag-expressing cell clone, respectively. (e) Anti-CD3 immunohistochemistry revealed an increase in the number of T-lymphocytes in the livers of mice that received AR71-HisTag-expressing cells. (f) Anti-caspase 3 immunohistochemistry indicated increased caspase 3-mediated apoptosis in the AR71-HisTag-expressing tumors. (g) Wild-type murine B16 melanoma cells were injected into the spleens of Bl/6N mice before treatment with i.v. injections of AR71 (n = 8 each). Histological analyses revealed a significant reduction in the average number of hepatic metastases in mice treated with AR71 as compared to untreated control mice. (h) Representative histological liver sections (upper row) and macroscopic pictures (lower row, magnifications in lower left corners) of untreated (control) and treated (AR71) mice. (i) Anti-CD3 immunohistochemistry revealed an increase in the number of T-lymphocytes in the livers of mice treated with AR71. (j) Anti-caspase 3 immunohistochemistry indicated increased caspase 3-mediated apoptosis in the tumors of mice treated with AR71. (*: p<0.05).