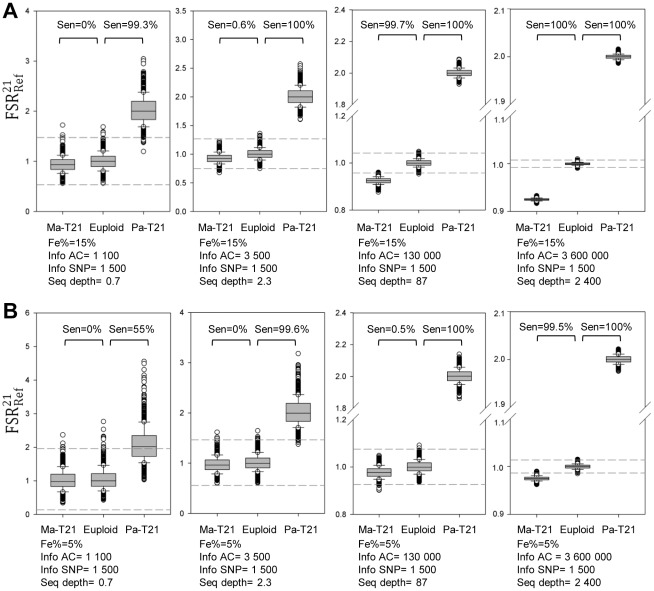
Figure 3. Computer simulation for T21 detection for fractional fetal DNA concentrations of 5% and 15%.
In order to obtain a specificity of greater than 99%, the cutoffs for T21 differentiation were chosen at 3 standard deviations above and below the mean F-S ratio of the euploid group. The sensitivity for paternally- and maternally-derived T21 detection was investigated on different numbers of informative allelic counts on chr21 and chrRef, respectively, for a fractional fetal DNA concentration of 15% (A). Similar analysis was performed for a fractional fetal DNA concentration of 5% (B). (Ma-T21: maternally-derived T21. Pa-T21: paternally-derived T21. Sen=sensitivity. Fe%=fractional fetal DNA concentration. Info AC=informative allelic counts on each of chr21 and chrRef. Info SNP=informative SNPs on each of chr21 and chrRef. Seq depth=sequencing depth. Info AC=Info SNP×Seq depth).