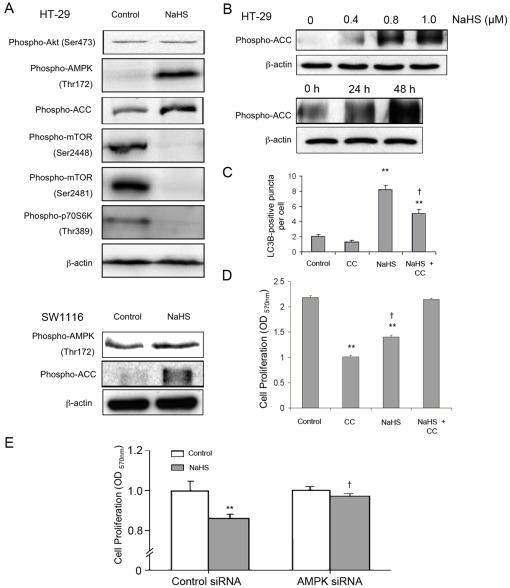
Figure 5. Involvement of AMPK/mTOR pathway.
(A) Treating colon epithelial cells with NaHS (1 mmol/L; 24 h) resulted in hyperphosphorylation of AMPK and hypophosphorylation of mTOR and p70 S6K. NaHS (1 mmol/L) also increased phosphorylation of acetyl-CoA-carboxylase (ACC) but did not affect Akt phosphorylation at Ser473. (B) NaHS dose- and time-dependently enhanced ACC phosphorylation in HT-29. (C) The AMPK inhibitor compound c (CC) significantly reduced the number of LC3B+ autophagic vacuoles in H2S-treated cells. HT-29 cells were treated with compound C (20 mmol/L) for 8 h followed by 1.0 mmol/L NaHS treatment for another 48 h. (D) Compound C (CC) reversed the inhibitory effect of H2S on HT-29 cell proliferation. (E) Knockdown of AMPK abolished the inhibitory effect of NaHS (1 mmol/L) on cell proliferation in HCT116. ** P<0.01, significantly different from respective control group. † P<0.05, significantly different from the NaHS group.