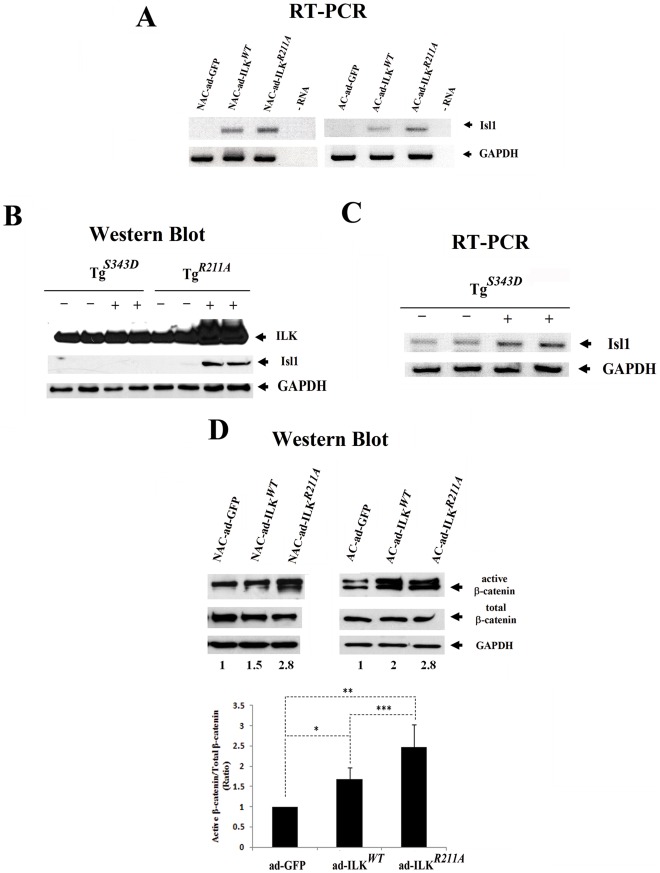
Figure 7. Over-expression of ILK induces Isl1 expression and β-catenin stabilization in vitro and in vivo.
(A) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis showing the Isl1 expression in adherent (AC) and non-adherent (NAC) cells derived from fetal myocardium transduced with ad-ILKWT, ad-ILKR211A or ad-GFP. GAPDH expression was also tested in all experimental groups. (B) Western Blot analysis of protein levels of ILK and Isl1 in myocardial lysates derived from transgenic mice with cardiac-restricted expression of constitutively active ILK (TgS343D) or mutant ILK (TgR211A) and their littermate controls. (C) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis demonstrating the Isl1 expression in hearts of transgenic mice with cardiac-restricted expression of constitutively active ILK (TgS343D) (+) compared to their littermate controls (−). (D) Western blot analysis showing the protein levels of stabilized, dephosphorylated β-catenin and total amount of β-catenin in adherent and non adherent fetal cardiac fractions infected with ad-ILKWT, ad-ILKR211A or ad-GFP. Each experiment was performed at least three times on independent samples and one representative blot with its corresponding expression ratios (active/total β-catenin expression) is shown at the top. The bar graph at the bottom summarizes the quantitative analysis of stabilized β-catenin expression in cells derived from fetal myocardium transduced with ad-ILKWT, ad-ILKR211A or ad-GFP. Data are mean ± SD, *p<0.007, **p<0.001, ***p<0.05.