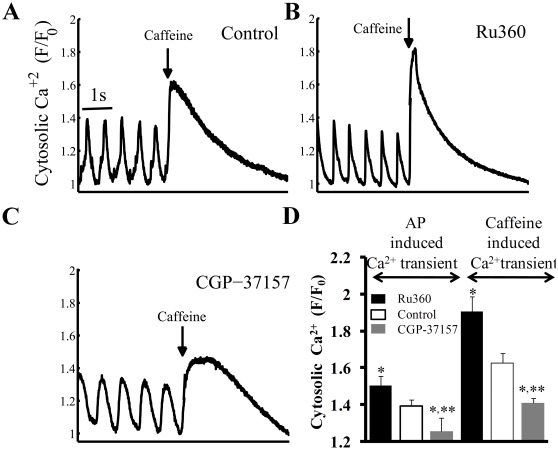
Figure 3. SR load estimation from rapid caffeine application.
Effects of a rapid application (“spritz”) of caffeine (indicated by the arrow) onto SANC (A) in control, or (B) in the presence of Ru360 or (C) CGP-37157. (D) Average effects of Ru360 or CGP-37157 on peak AP-induced cytosolic Ca2+ prior to a caffeine spritz (left), and the subsequent caffeine-induced cytosolic Ca2+ transient (right) (n = 12, for each group). (The caffeine response can be usually measured only once in a given SANC, because following caffeine application a prolonged period is required for AP firing rate to return to the control AP firing rate. Therefore, the effects of caffeine before (i.e. control) and following application of drugs that affect Ca2+ m flux were measured in different cells).