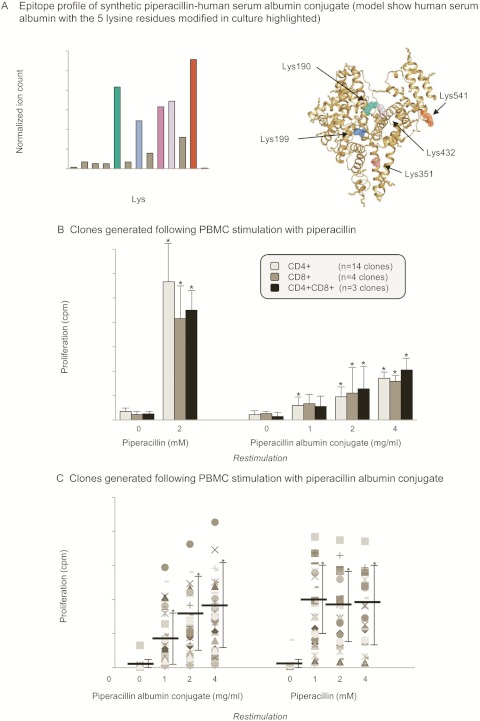
Fig. 6.
Stimulation of T-cell clones with a synthetic piperacillin albumin conjugate. A, epitope profile of the piperacillin-albumin conjugate. Lys residues modified in cell culture supernatant are highlighted in different colors. B, concentration-dependent proliferation of CD4+, CD8+, and CD4+CD8+ T-cell clones with the synthetic albumin conjugate. Clones were generated after PBMC stimulation with piperacillin. The cells were incubated for 2 days, and 0.5 μCi [3H]thymidine was added for the last 16 h of culture. The data show the mean ± S.D. of the indicated number of clones. *, p < 0.05 when drug antigen-treated wells were compared with control wells. C, comparison of piperacillin- and piperacillin-albumin conjugate-specific proliferation of T-cell clones. Clones were generated after PBMC stimulation with the piperacillin albumin conjugate. The cells were incubated for 2 days, and 0.5 μCi [3H]thymidine was added for the last 16 h of culture. The data show the mean ± S.D. of the indicated number of clones. *, p < 0.05 when drug antigen-treated wells were compared with control wells.