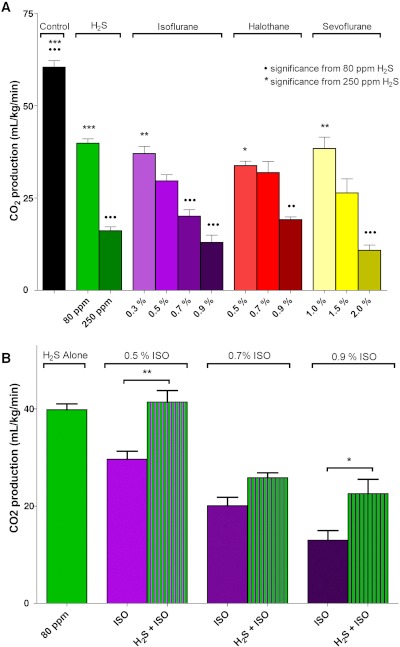
Fig. 3.
Rate of CO2 production in mice after breathing 15 min of H2S or volatile general anesthetics. A, each gas significantly decreased CO2 production, in a concentration-dependent manner, compared with control. ••, p < 0.01 and •••, p < 0.001 significance from H2S at 80 ppm. ★, p < 0.05, ★★, p < 0.01, and ★★★, p < 0.001 significance from H2S at 250 ppm. In terms of CO2 production, H2S at 80 ppm was essentially equivalent to 0.3% isoflurane, 0.5% halothane, and 1.0% sevoflurane; and H2S at 250 ppm was equivalent to 0.9% isoflurane, 0.9% halothane, and 2.0% sevoflurane. B, the addition of H2S at 80 ppm reduced (antagonized) the metabolic effect of each concentration of isoflurane (Iso). ★, p < 0.05; ★★, p < 0.01. Statistical analyses for both metabolic studies were performed by using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparison test.