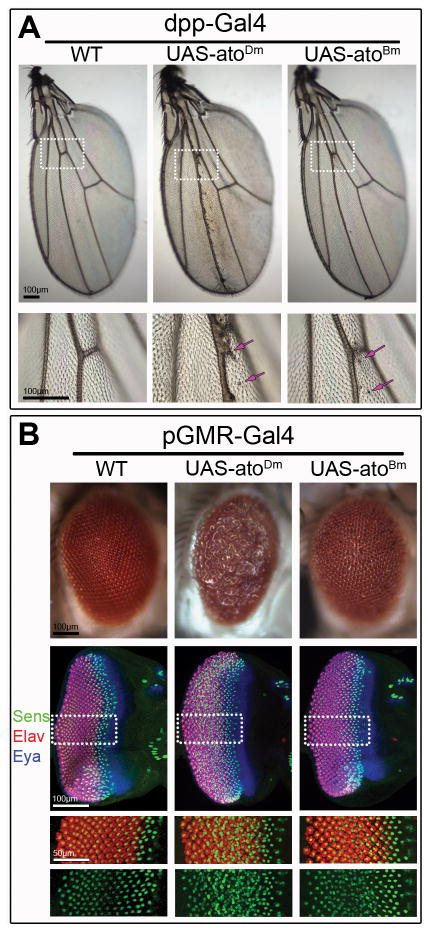
Figure 3. Mis-expression of AtoDm and AtoBm induces related phenotypes in the wing and the eye.
A) Mis-expression AtoDm or AtoBm in the developing wing disc under the control of dpp-Gal4 induces formation of ectopic chordotonal organs (arrow) along the 3rd wing vein. Lower panel shows high magnification of region marked in upper panel. B) Mis-expression AtoDm or AtoBm under the control of pGMR-Gal4 disrupts eye development leading to the formation of a ‘rough’ adult eye in which the spatial arrangement of the ommatidia is disrupted. Developing disc corresponding to the adult eyes shown above were stained for Sens to mark R8 neurons, the pan-neural marker Elav to highlight all photoreceptors and the retina-identity determinant Eya to mark the developing eye disc. Single channels for Sens and Elav are shown below. Misexpression of AtoDm or AtoBm results in the formation of supernumerary R8 neurons (Sens-positive). In both wing and eye, AtoDm has a stronger effect than AtoBm but the resulting phenotypes are consistent with a similar activity of the two proteins in these experiments.