Figure 5.
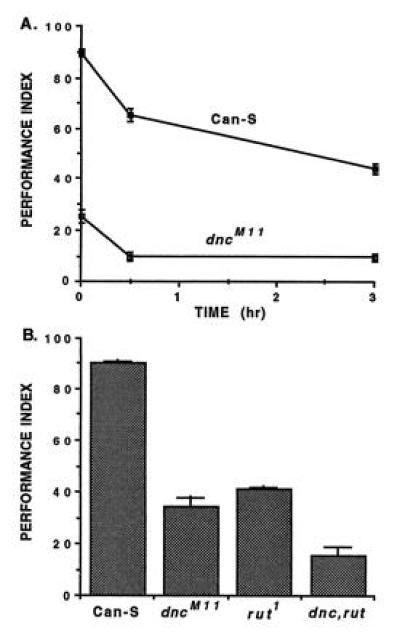
Olfactory learning and memory in normal and mutant flies. (A) Memory retention in wild-type (Can-S) flies or dunceM11 mutants. Each point represents the average avoidance responses of about 1200 individuals. The genetic backgrounds of each strain were heterogeneous and equilibrated, so the difference between mean scores represents the average effect of the dunceM11 mutation in homozygotes (see text). (Data from ref. 52.) (B) Learning in wild-type (Can-S), dunceM11 (dncM11) or rutabaga1 (rut1) single-gene mutants and dunceM11 rutabaga1 (dnc, rut) double-mutants. The learning defect in the double mutant is more severe than either single mutant, revealing a quantitative, polygenic basis for olfactory learning. (Data from ref. 38.)
