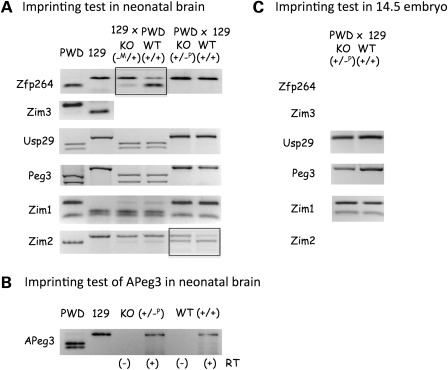
Figure 3.
Deletion effects on the imprinting status. (A and B) Imprinting test in neonatal brains. (C) Imprinting test in 14.5 dpc embryos. Two reciprocal crosses (129 × PWD, PWD × 129) were performed to derive the F1 hybrids with the maternal and paternal transmission of the KO allele, respectively. Each set of imprinting tests used two littermates (KO and WT). The digestion pattern of each gene's RT–PCR product by a given restriction enzyme was compared with that of two parental strains (PWD and 129). In the case of APeg3, total RNA from the littermates (KO and WT) of the PWD × 129 cross was analyzed with a strand-specific RT–PCR scheme (B). Two reactions for each RNA sample, RT(−) and RT(+) indicating without and with reverse transcriptase, respectively, were included to monitor genomic DNA contamination. We placed rectangles on the gene, the imprinting status of which was shown to be affected by the deletion of the Peg3-DMR.