Fig. 3.
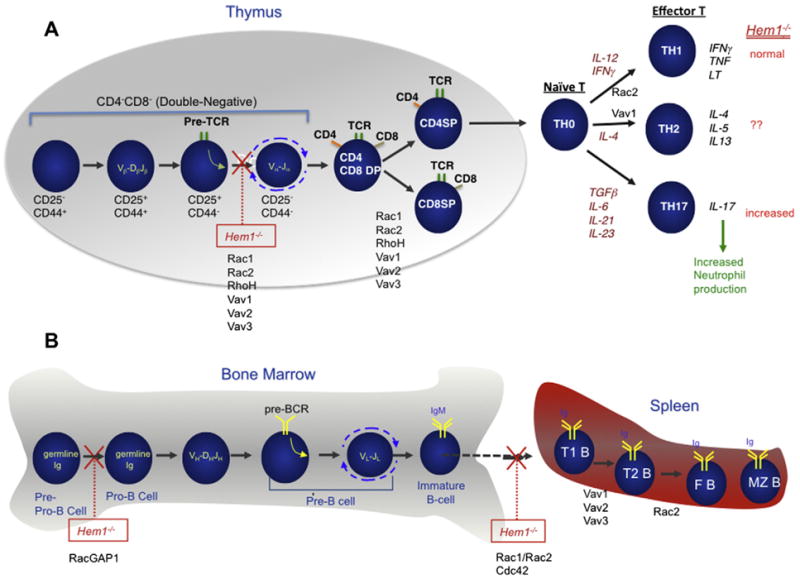
Roles of Hem-1 in lymphocyte development and function. (A) Schematic diagram of T cell development in the thymus and periphery. Successful in-frame rearrangement of T cell receptor β chain genes [V(variable)β-D(diversity)βJ(joining)β] in CD4−CD8− [double-negative (DN)] cells results in formation of the pre-TCR complex, which signals expansion, rearrangement of TCRα chain genes (Vα–Jα), and differentiation to the CD4+CD8+ double-positive (DP) cell state. Following in-frame TCRα chain rearrangement, TCRαβ expressing DP thymocytes undergo “positive selection” based on MHC class I- or against MHC class II-restriction, which drives selection of mature CD8+CD4− single-positive (SP) and CD4+CD8− SP cells respectively. SP cells then migrate into secondary lymphoid tissues, in preparation for encountering foreign antigens. DN cells are further subdivided into different stages of development based on expression of CD25 and CD44. Upon T cell activation, naïve CD4 T cells differentiate into distinct CD4 T cell subsets based on the local cytokine milieu. CD4 effector T cells (TH1, TH2, and TH17) produce their unique set of signature cytokines. Gene-targeted mutations of Hem-1, Rac (1 and/or 2), RhoH, or Vav (1,2, and/or 3) in mice result in arrest or impaired differentiation at different stages of T cell development in the thymus and periphery [10,13,74]. (B) Schematic diagram of B cell development in the bone marrow (and fetal liver). The earliest committed B cell progenitor (called a pre-pro-B cell) has its immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy and light chain genes in germline (unrearranged) configuration. The Ig heavy chain genes rearrange first (VH-DHJH) in pro-B cells. Following successful in-frame VH-DHJH rearrangement, the pre-B cell receptor (pre-BCR) is formed on the surface of pre-B cells, resulting in proliferation, differentiation and immunoglobulin light (IgL) chain gene rearrangement (VL-JL). Following successful VL-JL chain gene rearrangement, immature B cells leave the bone marrow for the spleen and lymph nodes where cells further develop into transitional B cells (T1 and T2) and mature B cells (follicular and marginal zone). Inhibition of Hem-1, Rac (1 and 2), RacGAP1, or Vav (1, 2, and 3) function results in arrest or impaired differentiation at different stages of B cell development [10,13].
