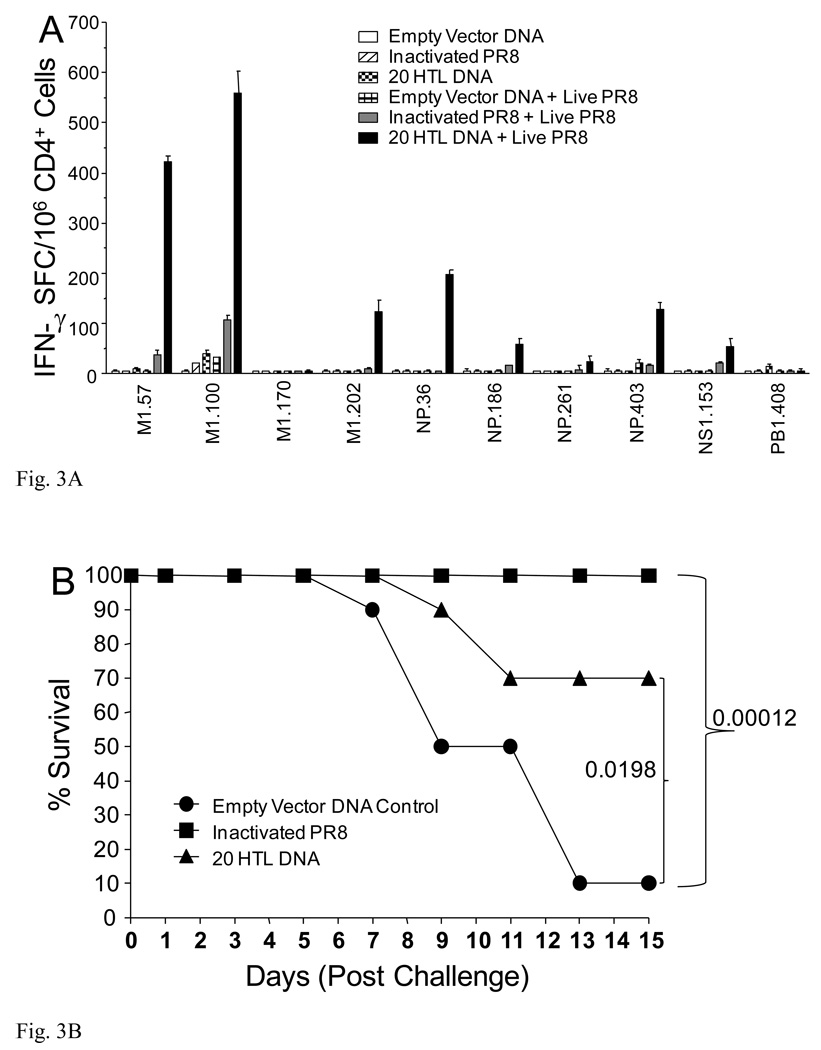
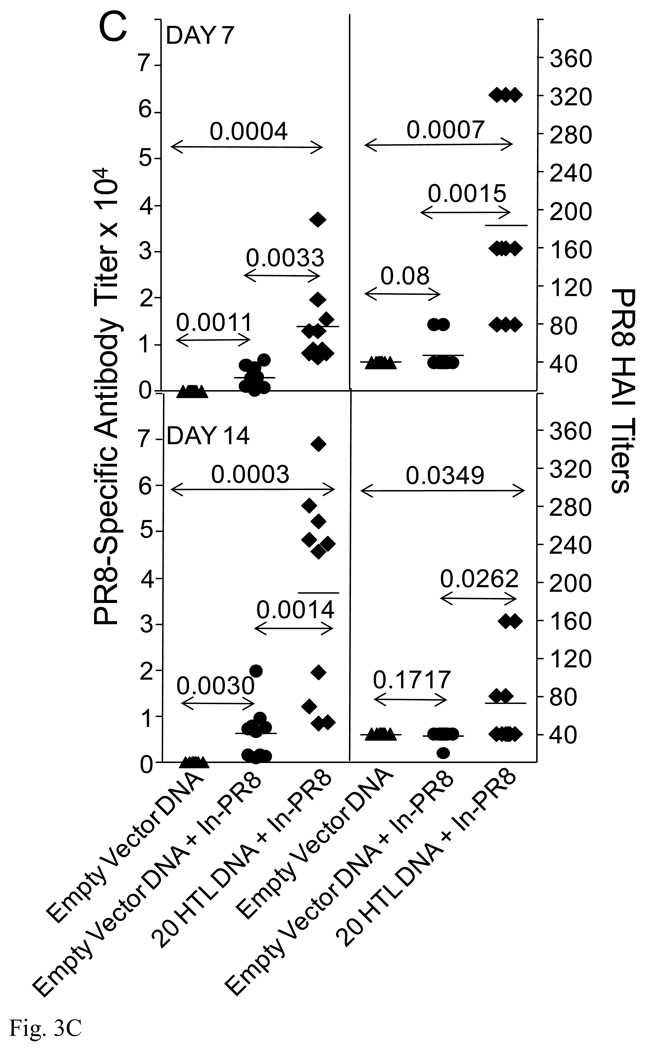
Fig. 3.
Epitope-specific immune responses, animal survival and augmentation of PR8-specific antibody responses. HLA-DR4 transgenic H-2b mice, (n=14), were immunized with CD4+20 epitope DNA construct or empty vector DNA control using Ichor’s in vivo electroporation device with 50 µg per mouse. Additional, a group of mice was also immunized with inactivated PR8. Two weeks post-immunization, two mice per group were sacrificed and splenocytes prepared for an epitope-specific IFN-γ ELISPOT (A). All 20 CD4+ epitope-specific responses were evaluated. Only positive responses plus three negative responses as comparators are shown. At this same time, the remaining 12 mice were infected with 100 HAU PR8 (4MLD50). Six days following the PR8 infection, two additional mice were sacrificed from each group for a second epitope-specific ELISPOT evaluation (A). The remaining 10 mice were monitored for survival of the animals (B). HLA-DR4 transgenic mice, (n=10) were immunized with CD4+20 epitope DNA vaccine or empty vector DNA control. Two weeks later, mice were immunized with 15 µg inactivated PR8. Seven and 14 days following inactivated PR8 immunization, mice were bled for determination of HA-specific antibody responses (C).