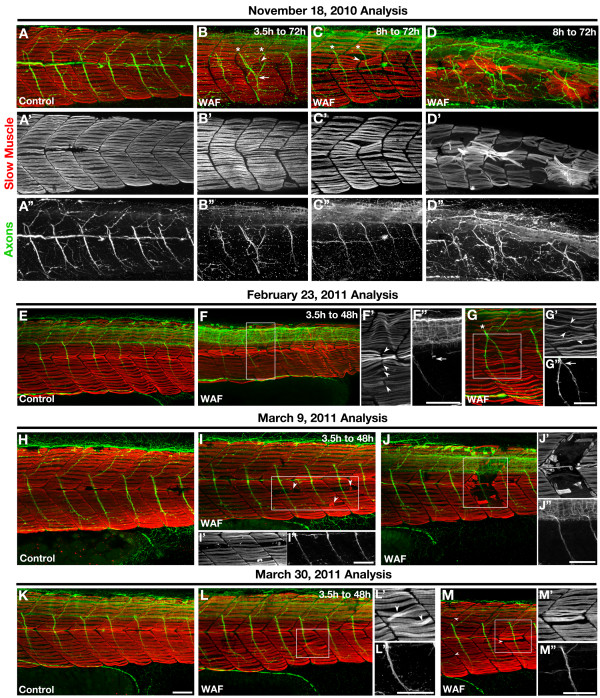
Figure 8.
The severity of deformations in slow-twitch skeletal muscle development decreased with each experimental replicate. (A-M) Lateral views of F59 labeled Myosin heavy chains in slow-twitch muscle fibers (red) and anti-Acetylated tubulin labeled motor axons (green) in the embryonic trunk at 72 hpf (A-D) and 48 hpf (E-M). (A-D) Initial Macondo crude oil WAF treatments beginning at either 3.5 hpf (B) or 8 hpf (C, D) and ending at 72 hpf showed severely defective neuromuscular phenotypes, such as improper somite boundary formation (B, C, arrowhead) or slow muscle loss and disorganization (D). Somite boundary defects associated with the middle or ventral portion of the somite correlated with motor axon pathfinding errors (B, asterisks, arrow; D). (E-M) Subsequent WAF treatments beginning at 3.5 hpf and ending at 48 hpf induced somitogenesis (F, G; F, G', arrowheads), slow muscle (I-M', arrowheads), and motor axon pathfinding (F, G; F", G", arrows) defects, however the severity of these defects decreased over time with each experimental replicate from November to March. (A-M) Primed letters represent single channel images of slow muscle (single prime) or axon (double prime) labeling for the whole image (A-D) or just the boxed regions (F, G, I, J, L, M). Scale bars = 50 μm, A-M".