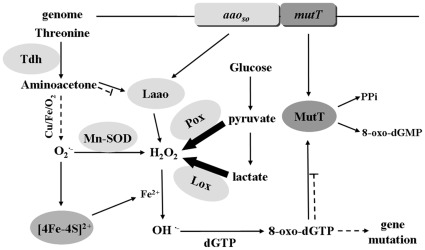
Figure 4. Depicted concerted working model of LAAO and MutT in preventing ROS-generated oxidative damage to cells.
aaoSo and mutT constitute an operon in S. oligofermentans and are co-transcribed, creating the equivalent protein products of the two. The absence of LAAO, an aminoacetone oxidase, was found to cause the accumulation of aminoacetone, which can be derived from threonine by threonine dehydrogenase (Tdh). It generates superoxide anions in the presence of oxygen and transition metals. Fe2+, released from proteins containing [4Fe–4S]2+ cluster by superoxide anion attack, was found to trigger the Fenton reaction to form hydroxyl radicals from H2O2, which is produced in abundance from lactate and pyruvate by Lox and Pox, respectively. These hydroxyl radicals oxidize nucleic acids, like dGTP to 8-oxo-dGTP, a mutagen that can cause severe gene mutations. The coexpressed MutT hydrolyzes 8-oxo-dGTP to the harmless 8-oxo-dGMP, and so prevents cell damage. LAAO, L-amino acid oxidase; MutT, pyrophosphohydrolase; Tdh, threonine dehydrogenase; Lox, lactate oxidase; Pox, pyruvate oxidase; Mn-SOD, manganese-dependent superoxide dismutase. Thick arrows refer to the main flux of H2O2; broken arrows indicate the conditional pathways.