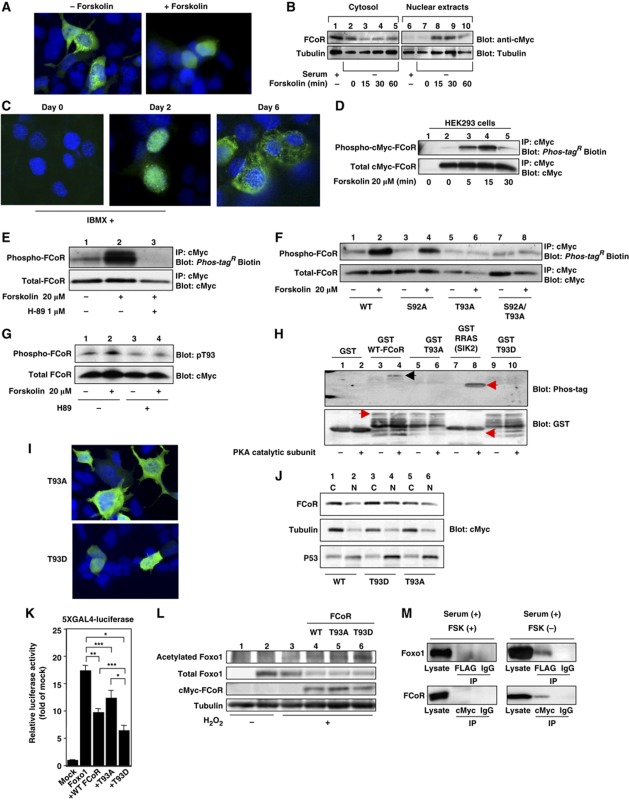
Figure 4.
FCoR is phosphorylated and translocated into the nucleus in a PKA-dependent manner. (A) Subcellular localization of exogenous FCoR in HEK293 cells. At 36 h after transfection with pCMV5-cMyc-WT FCoR, HEK293 cells were stimulated with forskolin (20 μM) for 30 min, fixed, and stained with anti-cMyc mouse monoclonal antibody. (B) Western blotting of cytosolic and nuclear extracts from HEK293 cells transfected with cMyc-FCoR. At 36 h after transfection with pCMV5-cMyc-WT FCoR, HEK293 cells were stimulated with forskolin (20 μM) at the indicated time and harvested. Lysates were fractionated into cytosolic and nuclear extracts and subjected to western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (C) Immunofluorescence of endogenous FCoR in 3T3-F442A cells. 3T3-F442A cells were cultured and induced differentiation into mature adipocytes as described in Materials and Methods except supplementation with 500 nM of IBMX for 48 h. Thereafter, cells were cultured in DMEM containing 10% fetal calf serum and 1.7 μM of insulin. Cells were fixed at the indicated days and stained with anti-FCoR rabbit polyclonal antibody. (D) Phosphorylation of FCoR by forskolin. After transfection with pCMV5-cMyc-WT FCoR, HEK293 cells were stimulated with forskolin (20 μM) at the indicated time and harvested. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-cMyc mouse monoclonal antibody, subjected to western blotting, and phosphorylated FCoR was detected. (E) Inhibition of phosphorylation of FCoR by H89. At 48 h after transient transfection with pCMV5-cMyc-WT FCoR, HEK293 cells were incubated with or without H89 (1 μM) for 3 h and stimulated with forskolin (20 μM) for 15 min and harvested. Phosphorylated FCoR was detected as described above. (F) Phosphorylation of mutant FCoR. After transfection with pCMV5-cMyc-WT (lanes 1 and 2), S92A (lanes 3 and 4), T93A (lanes 5 and 6), or S92A/T93A (lanes 7 and 8) FCoR, HEK293 cells were stimulated with forskolin (20 μM) for 15 min. Phosphorylated FCoR was detected as described above. (G) Detection of phosphorylated Threonine 93 by anti-phospho-T93-specific (anti-pT93) antibody. At 48 h after transfection with pCMV5-cMyc-WT FCoR, HEK293 cells were incubated with or without H89 (1 μM) for 3 h and stimulated with or without forskolin (20 μM) for 15 min and harvested. Lysates were subjected to western blotting with anti-pT93. (H) In-vitro phosphorylation assay of FCoR. GST, GST-WT, GST-T93A, GST-T93D FCoR, and GST-RRAS, which is a short sequence of salt-inducible kinase (SIK) 2, was phosphorylated in vitro by incubating with a catalytic subunit from cAMP-dependent protein kinase as described in ‘Materials and methods’. Reaction products were subjected to western blotting, phosphorylated products were detected using Phos-tagR BTL-104 (top panel) and then blotted with anti-GST antibody (bottom panel). (I) Subcellular localization of exogenous T93A (the top panel) or T93D FCoR (the bottom panel) in HEK293 cells. At 36 h after transfection with pCMV5-cMyc-T93A or T93D FCoR, HEK293 cells were fixed as described in Materials and methods and stained with anti-cMyc mouse monoclonal antibody. (J) Western blotting of cytosolic and nuclear extracts from HEK293 cells transfected with cMyc-WT (lanes 1 and 2), T93D (lanes 3 and 4), or T93A (lanes 5 and 6) FCoR. At 36 h after transfection, HEK293 cells were harvested. Lysates were fractionated into cytosolic and nuclear extracts and subjected to western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (K) 5XGAL4-luciferase assay of PM-Foxo1 with pCMV5/cMyc-WT, T93A, and T93D FCoR. At 36 h after transfection with pTAL-5XGAL4, phRL-SV40, and the indicated PM-Foxo1 with or without the FCoR expression vector, HEK293 cells were incubated with forskolin (20 μM) for 6 h and harvested. Luciferase activity was measured in the lysates. Data represent the mean values±s.e.m. from three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant difference (*P<0.001, **P<0.005, and ***P<0.05 by one-way ANOVA). (L) The T93D FCoR mutant acetylates Foxo1 the most. After transfection with pFLAG-CMV2-WT Foxo1 with or without pCMV5-cMyc-WT (lane 4), T93A (lane 5), or T93D (lane 6) FCoR, HEK293 cells were incubated with (lanes 3–6) or without H2O2 (lanes 1 and 2) (500 μM), nicotinamide (NAM) (50 mM), and trichostatin A (TSA) (2 μM) for 3 h and harvested. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG mouse monoclonal antibody (M2) and subjected to western blotting with the indicated antibodies. (M) Interaction between Foxo1 and FCoR. HEK293 cells were co-transfected with pCMV5-cMyc-Foxo1 and pFLAG-CMV2-WTFCoR and culture at the indicated condition. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG, anti-cMyc or normal mouse IgG and blotted with anti-cMyc or anti-FLAG antibody. Figure source data can be found with the Supplementary data.