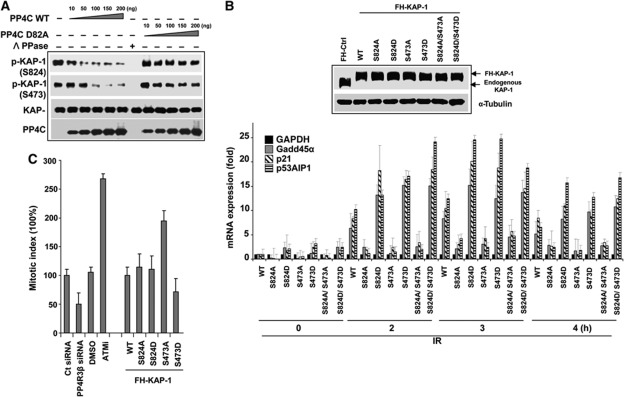
Figure 6.
PP4 directly dephosphorylates KAP-1 and impacts expression of stress-reponse genes and G2/M checkpoint. (A) PP4 dephosphorylates KAP1 in vitro. Wild-type PP4C and mutant PP4C (D82A) were purified using the baculoviral system and were serially diluted in the phosphatase reaction. λ phosphatase served as positive control for the reaction. PP4C dephosphorylates phospho-KAP1 on both S824 and S473 in a dose-dependent manner. Phosphatase reactions were probed with indicated antibodies. (B) PP4-mediated regulation of KAP-1 impacts the expression of Gadd45α, p21 and p53AIP1. In HeLa cells, endogenous KAP-1 was replaced with WT, mutant forms A (S824A or/and S473A) and D (S824D or/and S473D). After IR, cells were harvested and RNA purified at indicated times and quantitative real-time PCR (qRT–PCR) was performed. Data represent average and s.d. of four independent experiments. (C) Hyperphosphorylation of KAP1 on S473 impacts G2/M checkpoint. U2OS cells after depleting PP4R3β or replacing endogenous KAP-1 with wild-type, phosphonull mutants, or phosphomimetic mutants were exposed to irradiation (5 Gy) and then released in medium for 3 h and fixed. Mitotic cells were stained with anti-phospho-S10-Histone H3 (p-H3) antibody and quantified by flow cytometry. Data were analyzed with FlowJo software. The results from three independent experiments are graphically represented (S473A, P<0.029; S473D, P<0.011; PP4R3β, P<0.0321; ATMi, P<0.041). Figure source data can be found with the Supplementary data.