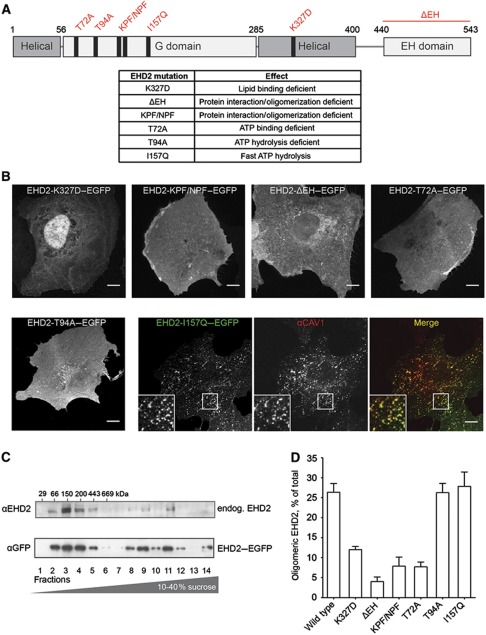
Figure 5.
Mutations in EHD2 impair association with caveolae and formation of large EHD2 complexes. (A) Domain structure of EHD2 with generated point and deletion mutants and table summarizing effects of these mutations described in previous studies (Guilherme et al, 2004; Daumke et al, 2007). (B) Confocal images of CV1 cells transiently expressing EGFP fusions of EHD2 mutants for 6–8 h. Cells were fixed and stained for endogenous CAV1 (only shown for EHD2-I157Q–EGFP as the other mutants did not colocalize with CAV1). Scale bar 10 μm. (C) Cell lysates prepared from 3T3-L1 cells or HeLa cells expressing EHD2–EGFP were run through 10–40% sucrose velocity gradients and fractions analysed by SDS–PAGE/western blot. In both cell lysates, EHD2 was present in distinct oligomeric species sedimenting at 8S, 60S, and 75S (Hayer et al, 2010a). 3T3-L1 fractions were analysed with anti-EHD2 antibodies and HeLa fractions with anti-GFP antibodies. (D) EHD2 mutants were analysed for their ability to form protein complexes with sedimentation coefficients >60S. EGFP fusions of mutant proteins were expressed for 6–12 h in HeLa cells and lysates run through sucrose velocity gradients (as in C). Fractions were analysed with anti-EHD2 antibodies. Bars present mean±s.e.m. of relative EHD2 signal in fractions 9–12 (‘oligomeric EHD2’) from three independent experiments.