Figure 3.
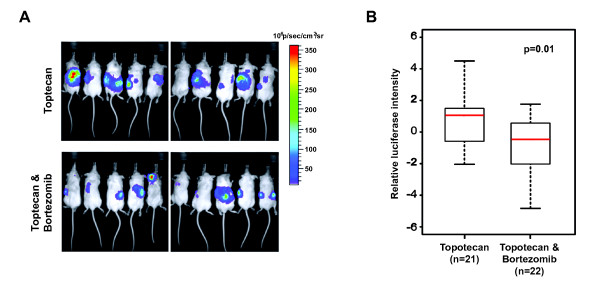
Delayed tumor progression in human neuroblastoma xenograft treated with topotecan and bortezomib. Mice were inoculated intravenously with five million SK-N-AS cells expressing luciferase. Seven days later, mice were treated with intraperitoneal injections of topotecan and bortezomib individually or in combination as detailed in methods. (A) Representative xenogen images of tumor-bearing mice. Mice receiving the combination of topotecan and bortezomib (lower panel) showed decreased tumor burden comparing those treated with topotecan alone (upper panel). Tumor burden was measured by imaging luminescence on a Xenogen IVIS 100 imaging system. (B) Quantification of tumor burden demonstrated that mice treated with combination of topotecan and bortezomib (n = 22) had significant less tumor burden than those treated with topotecan only (n = 21) (P = 0.01). This figure represents the results obtained from two independent experiments. We used relative luciferase signals in photons per second of the dorsal view of the two groups at two weeks post treatment. The log2 transformed luciferase intensities from each experiment are normalized using median-centered method and then combined. T-test was used to compare the difference of two groups