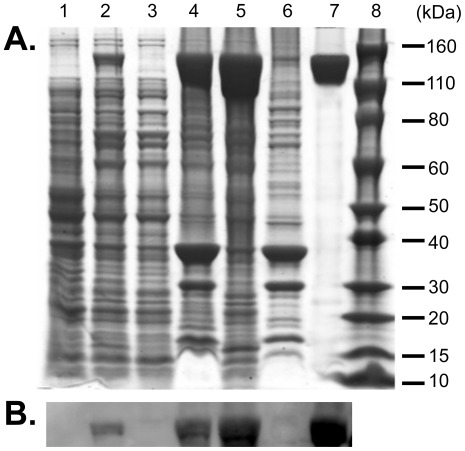
Figure 1. Fractionation and purification of recombinant Zbed4 protein expressed in E. coli cells.
A. SDS-PAGE. 50 µg/well of total protein from each fraction obtained in the expression, purification and refolding of Zbed4 were separated by SDS-PAGE on 4–12% Bis-Tris gels and stained with Coomassie R-250. Lane 1, whole E. coli lysate before IPTG induction. Lane 2, whole cell lysate after 6 h induction by IPTG. Lane 3, soluble proteins of E. coli cell lysate in HEPES buffer containing 1% Triton X100 and other components (see Materials and Methods), after passing through a French pressure chamber and centrifugation at 150,000 g. Lane 4, insoluble material (inclusion bodies) of lysate. Lane 5, solubilized inclusion bodies in 6 M Gu-HCl buffer 1, after centrifugation at 150,000 g. Lane 6, insoluble fraction of inclusion bodies. Lane 7, Zbed4 purified using BD Talon Co2+-activated affinity chromatography, after the refolding procedure and concentration. Lane 8, Novex Sharp (Invitrogen) standard protein markers. B. Detection of Zbed4 on Western blots using Penta His antibodies. Following SDS-PAGE, the separated proteins of each fraction were transferred to PVDF membranes and after blocking and incubation with Penta His antibodies conjugated with horseradish peroxidase, Zbed4 was visualized with the ECL Substrate of the Fast Western blot kit.