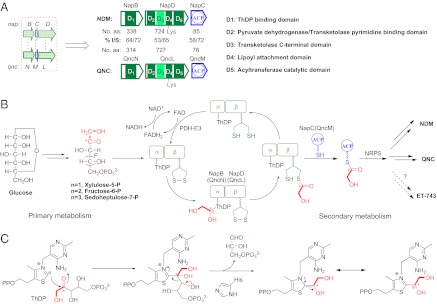
Fig. 2.
Proposed mechanism of the TKase-ACP systems involved in the tetrahydroisoquinoline biosynthesis by diverting a hydroxyacyl unit from ketosugars into a nonribosomal peptide assembly line. (A) Comparison between the TKase-ACP systems in NDM and QNC biosynthesis. aa, amino acid; I/S, identity/similarity. (B) The proposed biosynthetic pathway and catalytic cycle by TKase-ACP system. (C) The ThDP-dependent reaction mechanism catalyzed by TKase.