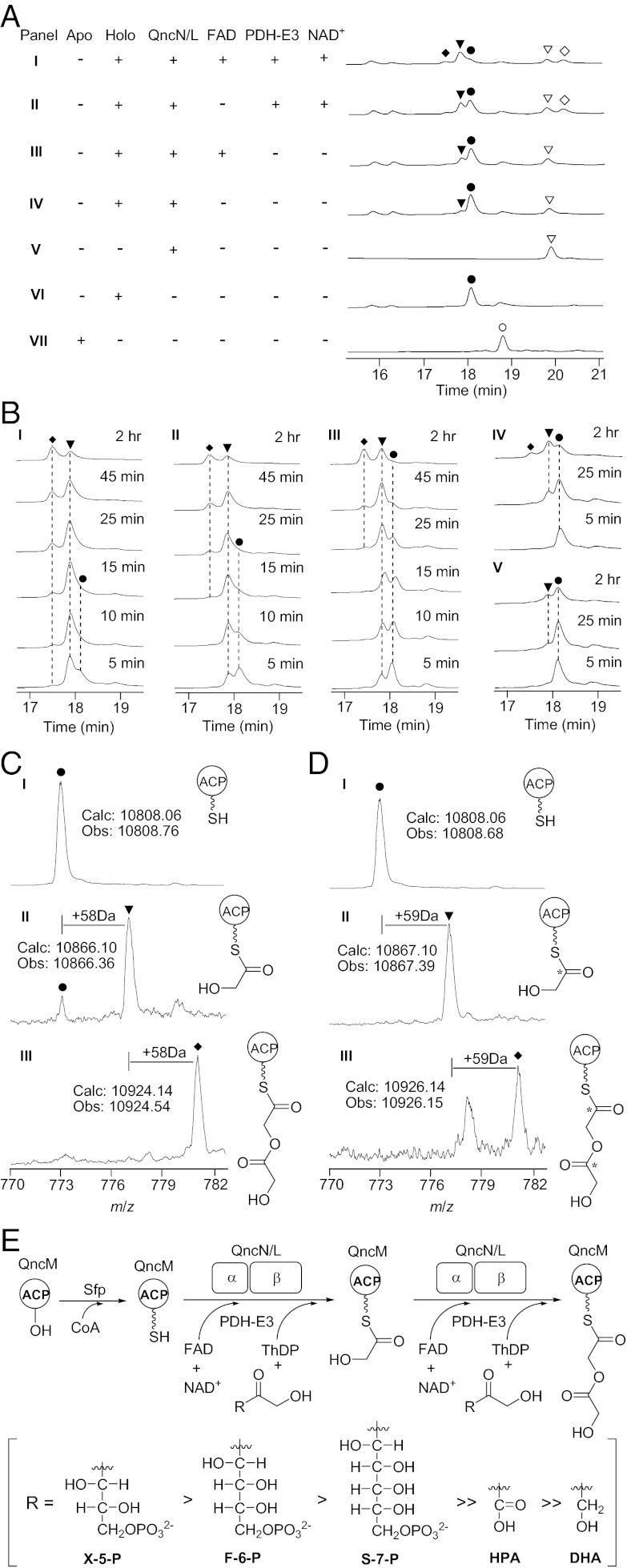
Fig. 5.
Biochemical characterization of the TKase-ACP systems in vitro. (A) HPLC analysis of enzymatic reaction. ○, apo-ACP; ●, holo-ACP; ▼, glycolicacyl-S-ACP; ◆, glycolicacyl-O-glycolicacyl-S-ACP; ▽, QncN or QncL; ◇, PDH E3. (B) Time course of enzymatic reaction using X-5-P (I), F-6-P (II), S-7-P (III), HPA (IV), and DHA (V) as donor substrates, respectively. The concentration of substrate used in the assay is 10 mM for DHA and 2 mM for others. (C) Q-TOF-MS analysis of holo-ACP (I), glycolicacyl-S-ACP (II), and glycolicacyl-O-glycolicacyl-S-ACP (III) using X-5-P as substrate. (D) Q-TOF-MS analysis of holo-ACP (I), glycolicacyl-S-ACP (II), and glycolicacyl-O-glycolicacyl-S-ACP (III) using [2-13C]F-6-P as substrate. (E) Proposed mechanism of the in vitro enzymatic reaction catalyzed by the TKase-ACP system.