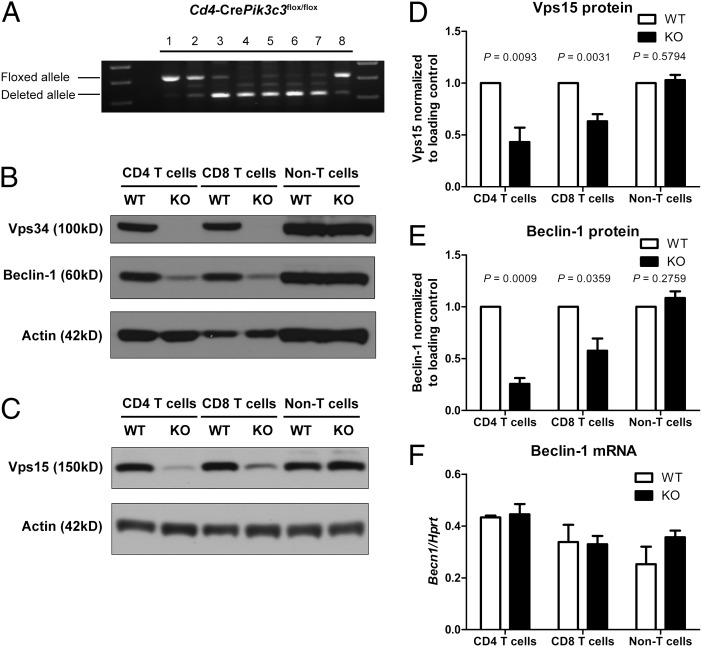
Fig. 1.
Deletion of Vps34 leads to disruption of the class III PI3K complex in T cells. (A) PCR analysis of genomic DNA from various cell populations isolated from Cd4-CrePik3c3flox/flox mice. 1, tail; 2, DN; 3, DP; 4, CD4 SP; 5, CD8 SP thymocytes; 6, peripheral CD4 T cells; 7, peripheral CD8 T cells; 8, non-T cells (mixture of B220+ NK1.1+ CD25+ CD11b+ CD11c+ cells). (B and C) Western blot analysis of Vps34 and Beclin-1 (B) and Vps15 (C) protein expression in CD4 and CD8 T cells as well as non-T cells from Cd4-CrePik3c3+/+ or Pik3c3flox/flox (WT) and Cd4-CrePik3c3flox/flox (KO) mice. Actin was used as a loading control. (D and E) Densitometry of Vps15 (D) and Beclin-1 (E) protein expression in Vps34 WT and KO cells as determined by Western blot analysis (n = 4–6). Amounts of Vps15 and Beclin-1 protein were normalized to actin and are relative to amounts in WT cells. (E) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of Beclin-1 mRNA expression in CD4 and CD8 T cells as well as non-T cells from Vps34 WT and KO mice (n = 3). mRNA expression was normalized to Hprt. Data are from one experiment (A), three independent experiments (F), or four to six independent experiments (B–E).