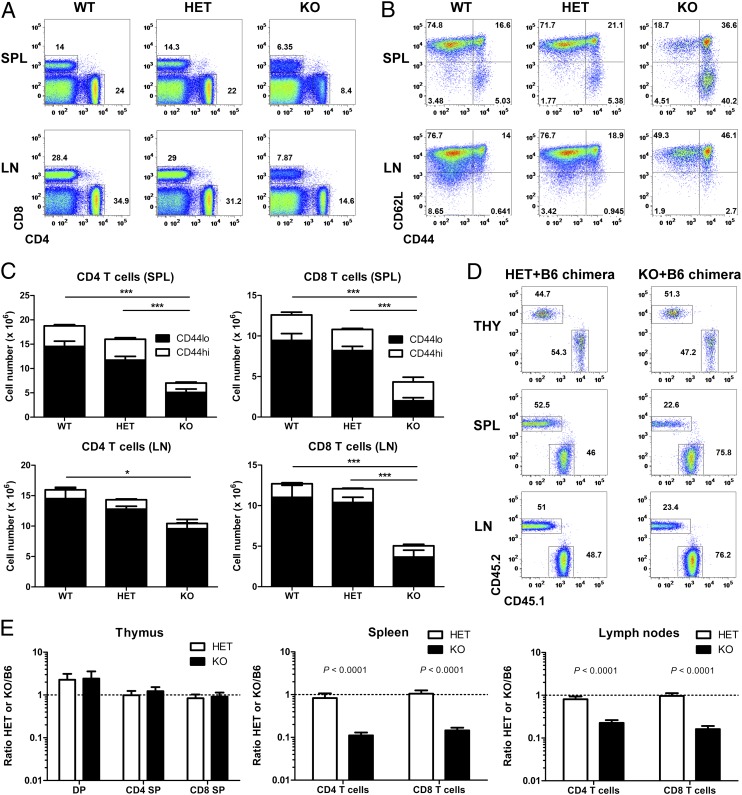
Fig. 3.
Vps34 is essential for the homeostasis of naïve T cells. (A) Representative FACS analysis of spleen (SPL) and LN cells from Vps34 WT, HET, and KO mice. Numbers next to outlined areas indicate percentages of CD4 and CD8 T cells. (B) Representative FACS analysis of CD8 T cells from Vps34 WT, HET, and KO mice. Plots are gated on CD8+CD4− cells. (C) Numbers of CD4 and CD8 T cells from Vps34 WT, HET, and KO mice (n = 8–13). P < 0.0001 for spleen CD4 T cells, P = 0.0404 for LN CD4 T cells, P < 0.0001 for spleen CD8 T cells, P < 0.0001 for LN CD8 T cells (one-way ANOVA). P values determined by Tukey’s multiple comparison test are indicated by asterisks (*P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001). (D) Representative FACS analysis of CD8 SP thymocytes (THY) and spleen (SPL) and LN CD8 T cells from Vps34 HET/B6 and Vps34 KO/B6 mixed BM chimeras at 8 wk postreconstitution. Plots are gated on CD8+CD4− cells. Numbers next to outlined areas indicate percentages of donor BM-derived HET or KO (CD45.2+) and B6 (CD45.1+) cells. (E) Ratio of various T-cell populations from thymus (THY), spleen (SPL), and LN cells in Vps34 HET/B6 and Vps34 KO/B6 mixed BM chimeras (n = 15–17). Results are combined from three independent experiments.